PAGE CONTENT:
Managing disk space efficiently has always been a critical part of maintaining a fast, responsive, and stable Windows system. As files accumulate - be it temporary files, leftover system updates, or unused downloads - disk clutter can gradually degrade system performance. To tackle this problem, Microsoft introduced Windows Storage Sense, a powerful, built-in feature designed to automatically free up space and keep your storage optimized without constant user intervention.

In this article, we'll take a deep dive into what Storage Sense is, how it works, how to configure it to suit your needs, and how it compares to traditional disk cleanup tools. Whether you're a casual PC user or a seasoned IT pro, understanding Storage Sense can help you better manage your system's health and longevity.
What is Windows Storage Sense?
Storage Sense is a disk management feature built into Windows 10 and Windows 11 that helps users automatically clear out unnecessary files from their system. It runs in the background based on a schedule or storage threshold to delete junk files, temporary items, system logs, Recycle Bin content, and more.
★ Key Features:
- Automated cleanup of temporary files.
- Periodic emptying of Recycle Bin.
- Management of files in the Downloads folder.
- Conversion of locally stored cloud content (e.g., OneDrive files) to online-only.
- Removal of outdated system and update files.
Storage Sense is a major step forward from the manual Disk Cleanup tool. It introduces automation and flexibility, making it easier than ever to manage disk usage without having to constantly check for space-consuming files.
How Storage Sense Works?
When enabled, Storage Sense continuously monitors your system's storage. It follows a set of user-defined rules to determine what data can be safely deleted, how often cleanups occur, and which files qualify for online-only storage if you're using OneDrive.
1. Temporary File Deletion
Storage Sense automatically removes:
- Windows temporary files.
- App leftover files (e.g., cache from Microsoft Edge or apps from the Store).
- Installer files and logs after updates.
- Old thumbnails and preview cache.
2. Recycle Bin and Downloads Folder
You can set Storage Sense to delete files that have been in the Recycle Bin or Downloads folder for a specified number of days (1, 14, 30, or 60 days). This helps prevent these folders from becoming long-term data hoarders.
3. OneDrive Cloud Management
Storage Sense can intelligently convert unused OneDrive files into "online-only" files. If a file hasn't been accessed in a certain number of days, Windows will remove the local copy (while retaining it in the cloud), freeing up local storage space.
4. Update Cleanup
When new updates are installed, Storage Sense can automatically delete old Windows update files and logs that are no longer needed, saving gigabytes of space.
How to Enable and Configure Storage Sense?
Storage Sense is highly customizable, allowing you to tailor its behavior to your usage patterns. Here's how you can enable and configure it:
Step 1: Open Storage Settings
To begin, open the Windows Settings panel:
- Press Windows + I on your keyboard to launch Settings.
![Windows Storage Sense]()
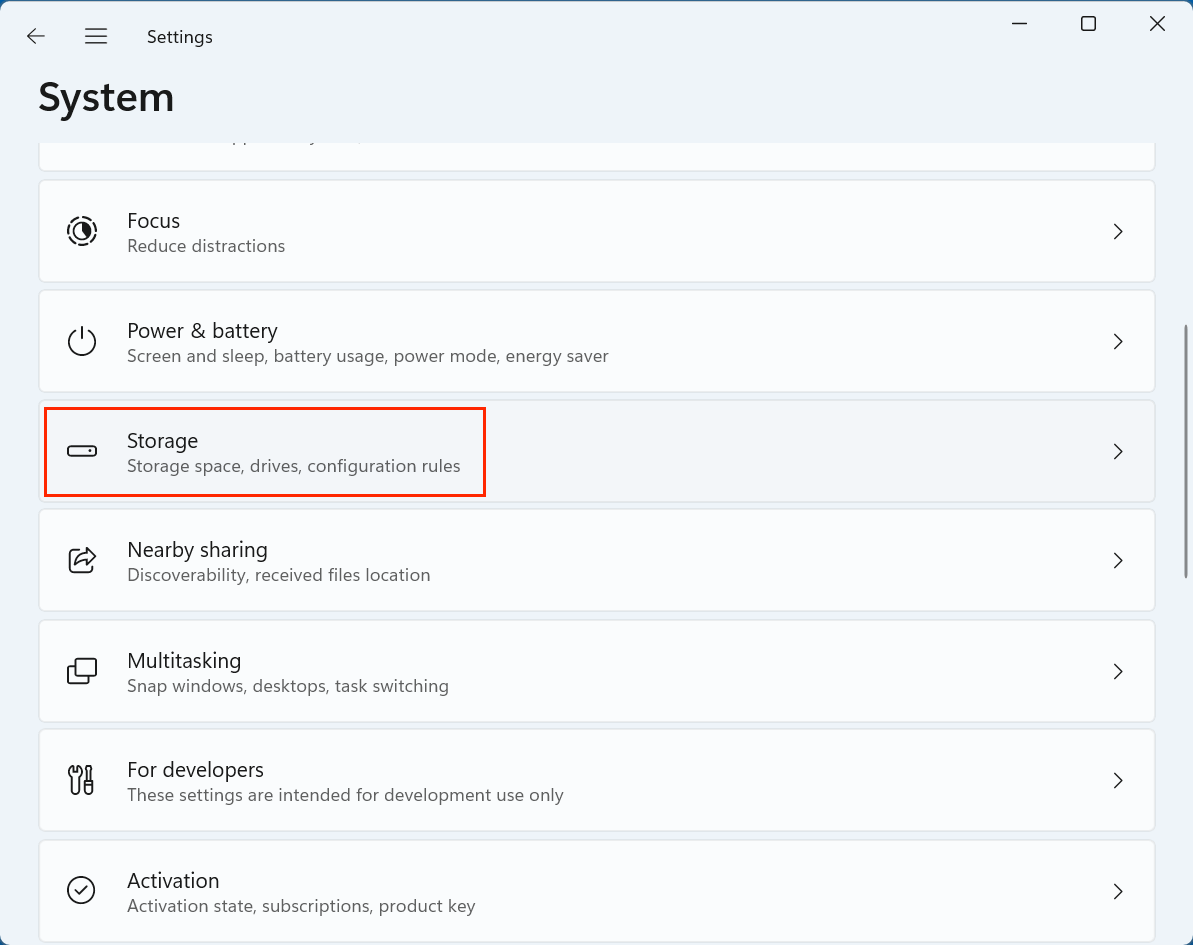
- Navigate to System > Storage on the left-hand menu.
![Windows Storage Sense]()
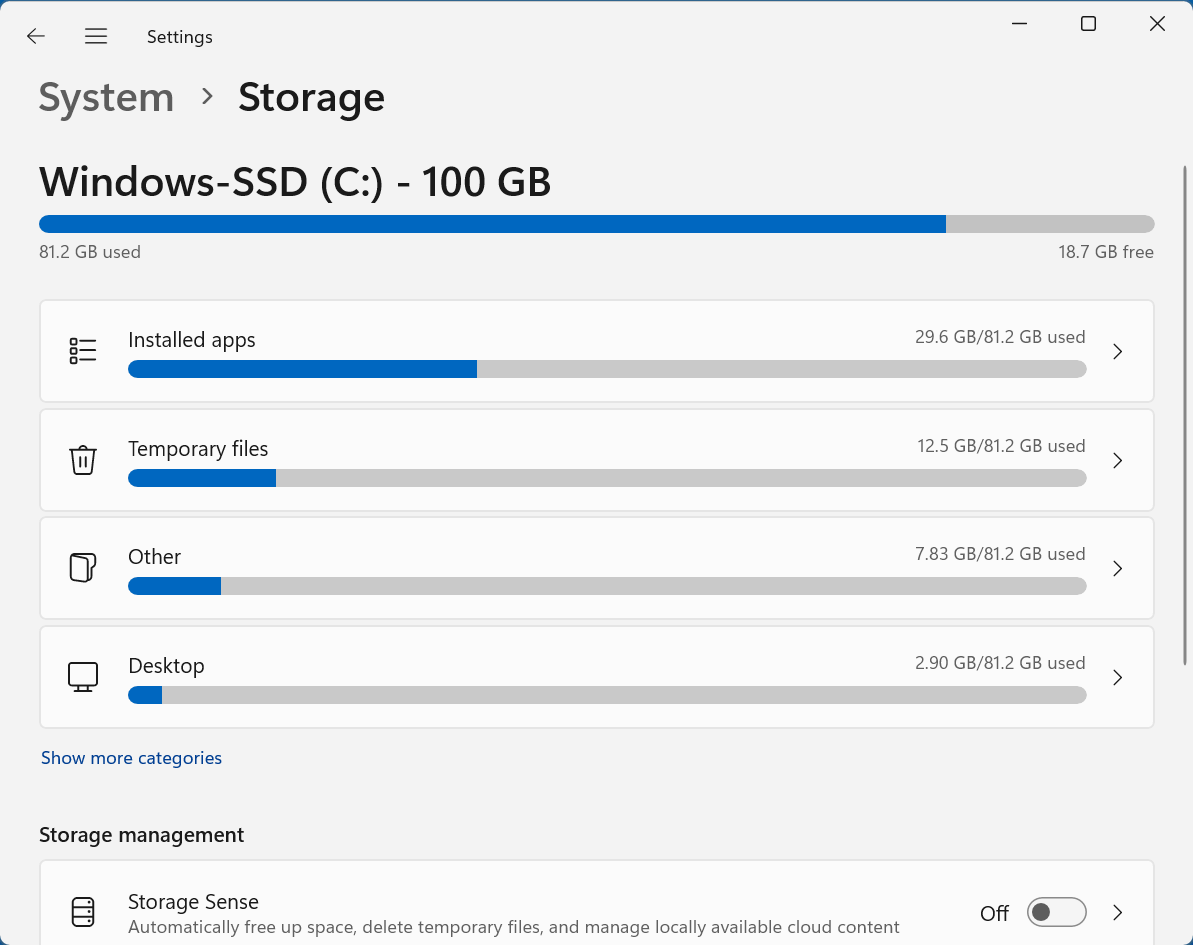
- You'll now see a detailed overview of how your storage is being used.
![Windows Storage Sense]()
This section gives you a breakdown of the major categories like:
- Installed Apps
- Temporary files
- Other
- Desktop
...
At the top of this page, you will also see Storage Sense listed under Storage Management.
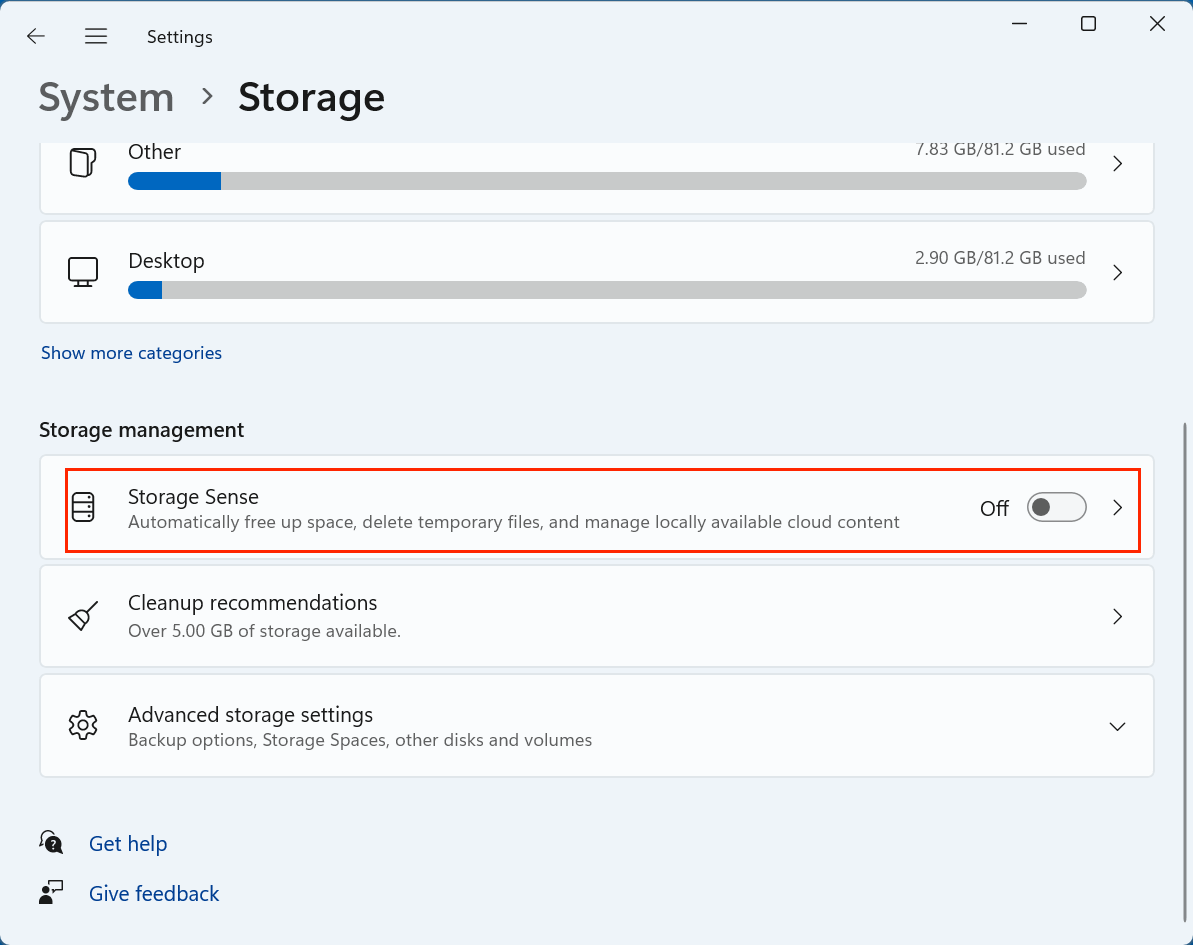
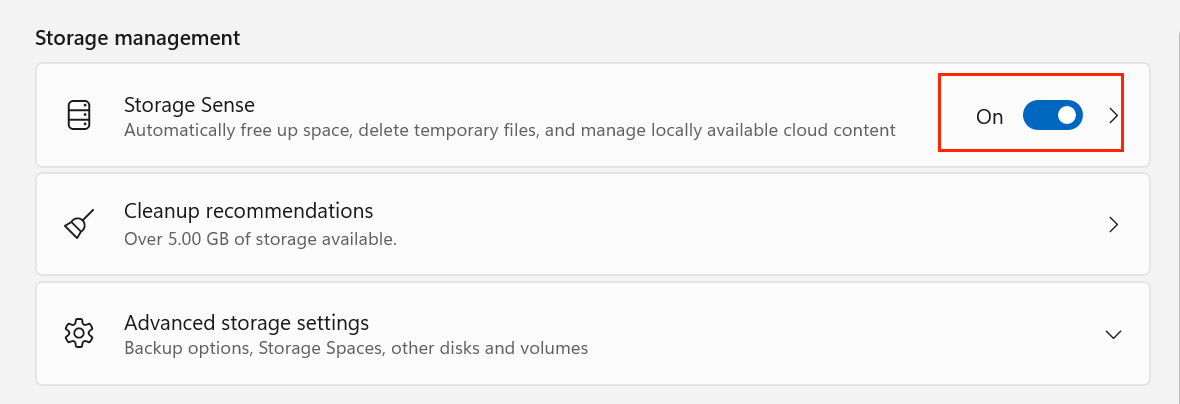
Step 2: Turn On Storage Sense
To activate Storage Sense:
- Locate the Storage Sense toggle switch.
- Flip the switch to On.
![Windows Storage Sense]()
This activates the default cleanup process, which will run automatically whenever your system is low on storage. However, for maximum benefit, you'll want to customize how it works.
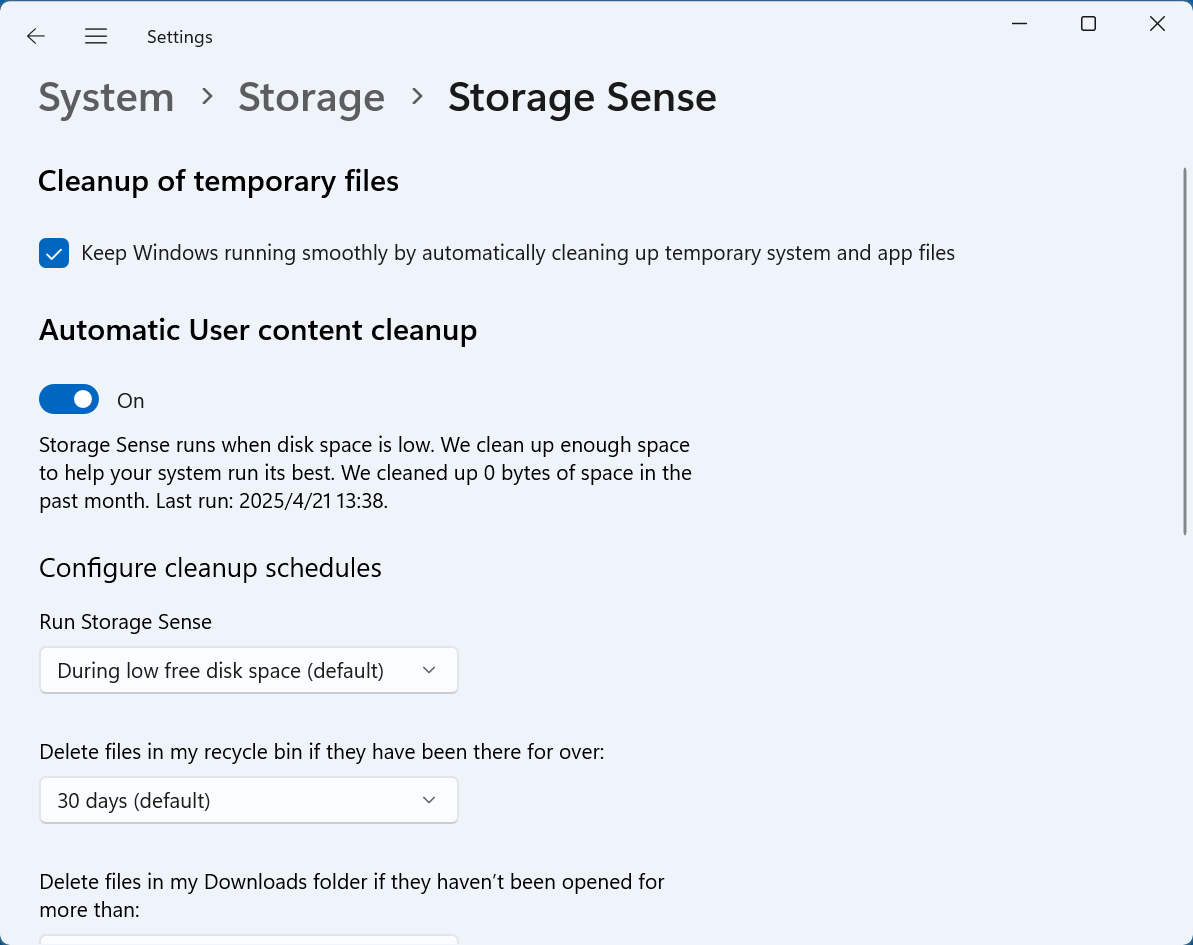
Step 3: Customize Storage Sense Behavior
Click Storage Sense. This brings you to a detailed configuration screen where you can fine-tune the feature's behavior.
1. Run Storage Sense: Choose Frequency
You can decide how often Storage Sense will run:
- Every day
- Every week
- Every month
- During low free disk space
![Windows Storage Sense]()
💡 Tip:
- If you're using a small SSD (128GB–256GB), setting it to run daily or weekly can keep space usage in check.
- For larger drives or systems with moderate usage, monthly may be sufficient.
2. Temporary File Cleanup
Check the option "Keep Windows running smoothly by automatically cleaning up temporary system and app files."

This allows Storage Sense to automatically clear out:
- Cache files from browsers and other apps.
- Installation logs.
- Old thumbnails.
- App temporary folders.
These files serve short-term purposes and can safely be removed to reclaim space.
3. Recycle Bin Management
Select a timeframe under "Delete files in my Recycle Bin if they have been there for over:"
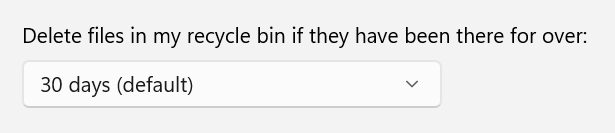
Options include:
- Never
- 1 day
- 14 days
- 30 days
- 60 days
💡 Tip:
If you regularly forget to empty the Recycle Bin, set this to 14 or 30 days. It keeps things tidy without removing recent deletions you might still need.
4. Downloads Folder Management
Select a timeframe under "Delete files in my Downloads folder if they haven't been opened for more than:"
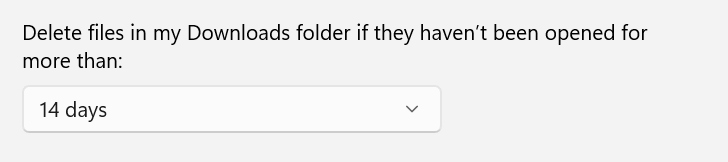
Options include:
- Never
- 1 day
- 14 days
- 30 days
- 60 days
💡 Important Note:
Many users store important files in Downloads, so use this setting carefully. If you rely on the Downloads folder for archiving, leave this set to Never or consider periodically moving files elsewhere.
5. OneDrive Cloud Content Settings
If you use OneDrive, Storage Sense can also manage cloud storage by making files "online-only" after a certain period of inactivity.
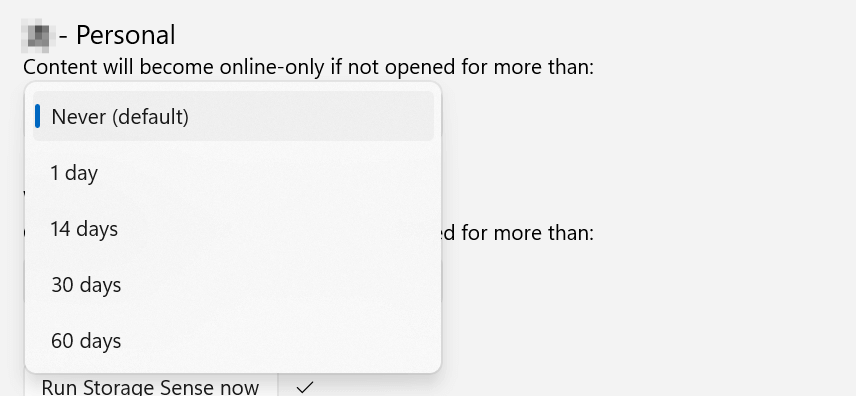
Choose from:
- Never
- 1 day
- 14 days
- 30 days
- 60 days
When set, this will:
- Retain the file in OneDrive.
- Remove the local copy to free up space.
- Re-download the file on-demand when needed.
Example:
If you haven't opened a file in 30 days, it becomes online-only. The file icon will remain, but it won't take up disk space.
Step 4: Run Storage Sense Manually
At the bottom of the settings page, there is a button labeled "Run Storage Sense now."
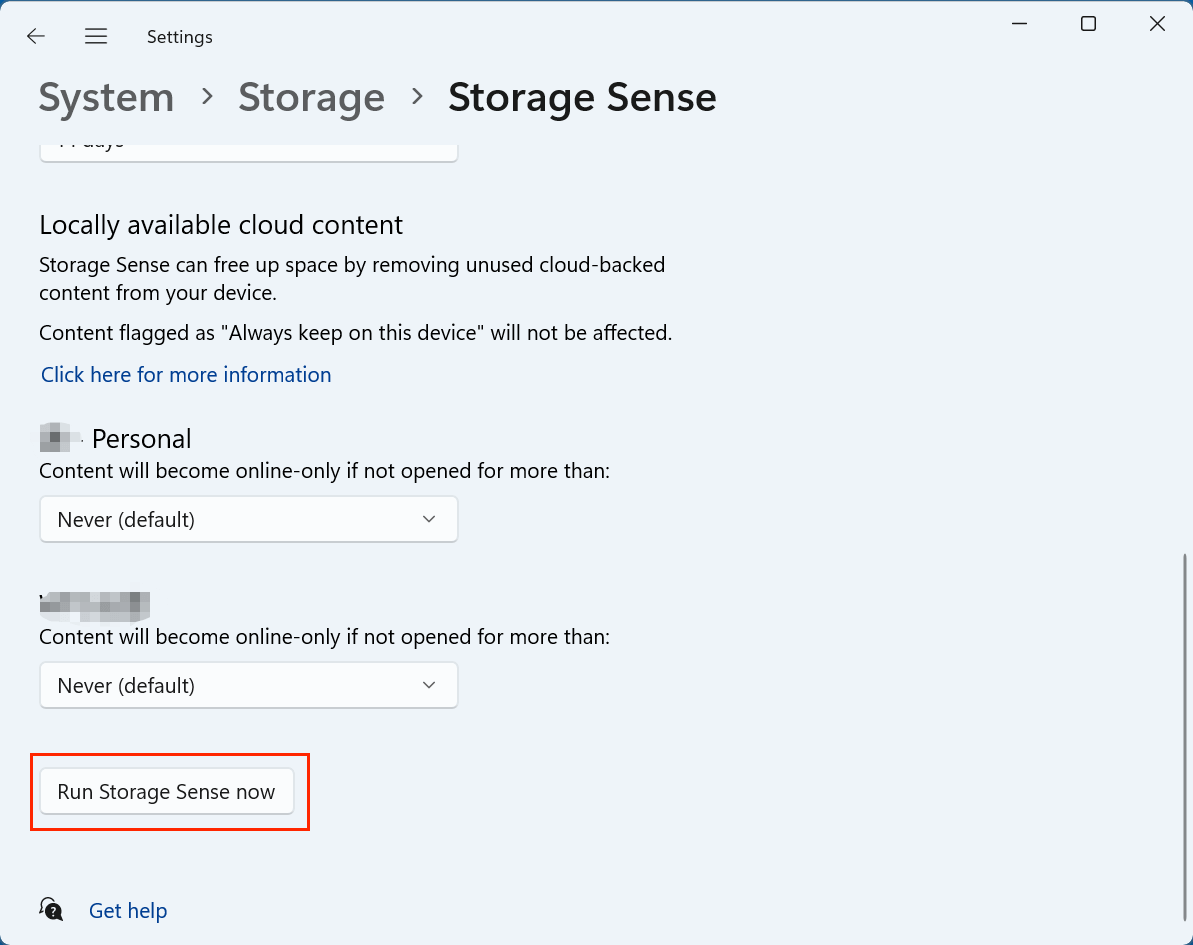
Clicking this will trigger an immediate cleanup based on your chosen settings. It's a great way to test how the feature works or to perform a one-time cleanup when you're running low on space.
Storage Sense vs. Manual Cleanup Tools
Before Storage Sense, Windows users typically relied on Disk Cleanup or third-party tools like Cleaner to reclaim space. Here's how Storage Sense stacks up:
| Feature | Storage Sense | Disk Cleanup | Third-Party Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automation | Yes | No | Optional |
| Cloud Integration | Yes (OneDrive) | No | Limited |
| Temporary File Deletion | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| text | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| App Cache Management | Yes | No | Yes |
| User Configuration | High | Low | High |
Pros of Storage Sense
- Built-in and safe to use.
- Fully automatic.
- Integrated with Windows updates and OneDrive.
- No need to install extra software.
Cons
- Lacks some deep-cleaning capabilities of third-party tools.
- Not available in Windows versions prior to 10.
- Fewer analytics and reporting features.
Advanced Storage Sense Features
Storage Sense continues to evolve, especially in Windows 11, where it gains deeper integration and more intuitive controls.
1. OneDrive Integration
Storage Sense identifies inactive cloud files and reverts them to online-only versions without deleting user data. This ensures your local storage is not clogged with seldom-used files while keeping them accessible via the cloud.
2. Windows Update Cleanup
After major Windows updates, previous versions are stored for rollback purposes. Storage Sense can automatically delete these after a few days (usually 10), saving several GB of space.
3. Delivery Optimization Files
Windows uses peer-to-peer delivery optimization for updates. Storage Sense can remove residual files from this system, which often go unnoticed.
4. Modern UI and Recommendations
In Windows 11, Storage Sense is enhanced with a cleaner UI and storage recommendations, offering suggestions such as:
- Deleting unused apps.
- Moving large files to another drive.
- Compressing unused files with NTFS compression.
Troubleshooting Storage Sense Issues
Like any automated tool, Storage Sense may occasionally encounter issues. Here are common problems and how to resolve them:
1. Storage Sense Isn't Running Automatically
- Fix: Ensure it is enabled and the frequency is set properly.
- Check: Scheduled cleanups won't occur if your PC is turned off or asleep during scheduled times.
2. Files Not Deleted as Expected
- Fix: Make sure cleanup options for Recycle Bin, Downloads, etc., are configured correctly.
- Files are only deleted if they meet the specified age criteria.
3. Storage Sense Greyed Out
- Fix: This might occur on PCs managed by organization policies (Group Policy/Intune). Check with your IT administrator or review local group policy settings under:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Storage Sense
4. OneDrive Files Not Converting to Online-Only
- Fix: Ensure that OneDrive is set to "Files on Demand" mode. Without it, Storage Sense won't be able to manage cloud content.
Tips for Efficient Storage Management Using Storage Sense
To make the most of Storage Sense, consider the following tips:
1. Choose the Right Frequency
- Heavy users: Run daily or weekly.
- Casual users: Monthly should suffice.
- Low disk space systems: Enable "Run during low disk space" for automatic intervention.
2. Don't Rely Solely on Downloads Folder
- If you use your Downloads folder for important files, avoid automatic deletion or back them up regularly.
3. Pair with Other Storage Tools
- Use "Storage Usage by Other People" and "Advanced Storage Settings" in Windows to identify space hogs.
- Consider moving large apps or games to another drive using Apps & Features.
4. Regularly Check for Update Debris
- Even with Storage Sense, manually check for leftover Windows.old folders after major updates, as they can take up 20–30GB.
Conclusion
Windows Storage Sense is a powerful yet often underutilized feature that can significantly improve disk hygiene with minimal user input. Whether you're constantly hitting low storage warnings or simply want to keep your system lean and efficient, Storage Sense provides a safe, smart, and seamless way to automate your disk cleanup routines.
By understanding its capabilities, configuring it to fit your habits, and combining it with other system tools, you can ensure that your Windows device remains clutter-free and high-performing. So, take a moment today to enable and tailor Storage Sense - it might just save you from your next storage crisis.
If Storage Sense deletes wrong files from your computer, you can use data recovery software - such as Donemax Data Recovery to recover the deleted or emptied files.


Donemax Data Recovery
One of the best data recovery programs to recover deleted, formatted or lost data from PC, Mac, HDD, SSD, USB drive, SD card, camera, RAID, Sever or other storage devices.
Related Articles
- Feb 26, 2025Fix Memory Stick Not Showing Up on Windows Without Losing Data
- Feb 20, 2025Convert RAW to NTFS with CMD (Command Prompt) – A Complete Guide
- Jun 25, 2025Fix 'CHKDSK Cannot Open Volume for Direct Access' Error
- Oct 11, 2024How to Format a Drive to exFAT?
- May 22, 2025How to Prevent Data Loss?
- Feb 17, 202510 Fixes for Fixing External Hard Drive Not Showing Up in File Explorer or This PC

Steven
Steven has been a senior writer & editor of Donemax software since 2020. He's a super nerd and can't imagine the life without a computer. Over 6 years of experience of writing technical solutions and software tesing, he is passionate about providing solutions and tips for Windows and Mac users.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems