PAGE CONTENT:
Choosing the right file system when setting up a new hard disk, external drive, or USB device can be a dilemma. While multiple options exist, NTFS stands out as the most widely used, versatile, and recommended format, offering broad compatibility across different storage media.

To be sure, are you familiar with this file system? What is NTFS file system and how NTFS works? When should you utilize it, and what are the benefits and drawbacks of doing so? If you stick around, we'll give you a comprehensive breakdown of the NTFS file system. Now, then, let's get started.
New Technology File System
The Windows NT operating system utilizes the New Technology File System (NTFS) as its default file system. It accesses and stores data on the hard drive. In addition to introducing new features like security access control (ACL), dependability, disk space utilization, and file system journaling, the file system also offered revolutionary data structures that enhanced performance and metadata.
The OS/2 High-Performance File System and the Windows 95 file allocation table (FAT) were utilized by MS-DOS and older operating systems before the introduction of the NTFS. Windows 2000, XP, and Windows Server 2003 all use NTFS.
Key Improvements:
✦ Stronger Opening: "Choosing the right file system" is more direct than "There's always the dilemma."
✦ More Concise: "When putting up" is replaced with "when setting up," which is more natural.
✦ Better Flow: The contrast between the initial dilemma and NTFS's advantages is clearer.
✦ Enhanced Readability: "Widely used, recommended, and visible" is reworded to avoid redundancy while keeping the emphasis.
✦ More Persuasive: "Stands out as the most widely used, versatile, and recommended format" strengthens the argument for NTFS.
Data Storage In NTFS
Here, we'll go over the inner workings of the file system and the partition's method of storing and backing up files. Let's start with the basics and figure out how the NTFS file system structures and organizes files.
An NTFS file system has five main parts: the Operating System Boot Record, the Master File Table (MFT) 1, the MFT Metadata, the MFT 2, and the Data Area.
Examine the function of each component:
- Partition Boot Sector: It stores boot data and is abbreviated as PBS (Partition Boot Sector).
- Master File Table: MFT, or Master File Table, is a directory that keeps the information about files, known as metafile data (or metadata), such as the file name, access rights, creation date, size, etc.
- Metafiles: Metafiles are useful for several reasons, including but not limited to: defining and organizing the file system, backing up important data in the file system, buffering changes to the file system, managing the allocation of free space, and structuring metadata.
- Data Area: The term "data area" refers to a partition or external drive section containing actual data.
When Should You Use NTFS?
Since Windows XP, NTFS has been the default file system for Microsoft operating systems. Starting with Windows Vista, it is mandatory to use NTFS formatting on the OS disk. This makes it reasonable, considering NTFS's many benefits over older FAT file systems like FAT32 and FAT16.
The NTFS file system is designed with network utilization in mind. As such, it can take full advantage of its clean architecture, including reasonable restrictions on individual users' visibility and modification permissions.
Although FAT32 is still used for certain modern-day applications, NTFS has several significant advantages. We've seen a significant increase in the maximum partition size, which is currently close to 16 terabytes.
As of 2020, only a small fraction of the market's hard drives can match this storage capacity, which is true for traditional mechanical HDD drives and cutting-edge SSD flash storage media.
The Pros And Cons Of Using NTFS
You'll find a list of benefits and drawbacks down below.
Pros
- Disk quotas are one of the main features because they give administrators more control over how much data may be stored on each user's hard drive. Disk quotas are a tool for system administrators to control how much space each user can use.
- The file system makes advantage of file compression to facilitate faster information transfers and more ample storage for enterprises. Additionally, huge files are supported.
- With NTFS's rights and access control capabilities, administrators may limit who can see important information. Additionally, encryption is supported.
- The MFT records all file activity on the disk, including deletions, additions, and modifications, so that administrators may monitor how files are being used. To keep track of what has happened, this file system keeps a diary.
- Due to NTFS's consistent file system, data and files may be promptly recovered in the case of a system failure or malfunction. A secondary MFT mirror file is available if the primary MFT becomes damaged, making this system fault resistant.
Cons
- The biggest drawback of NTFS is that it is exclusively read-only on non-Windows operating systems.
- Many portable gadgets, including Android phones, DVD players, and digital cameras, don't work with NTFS. Other gadgets, such as media players, smart TVs, and printers, don't support it.
- Unfortunately, OS X devices' compatibility with NTFS disks is restricted to reading only; they cannot create new files on NTFS volumes.
Conclusion
Newer versions of Windows and Windows Server rely on NTFS as their main file system because of its comprehensive feature set, which includes security descriptors, disk quotas, encryption, and rich metadata. Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) and NTFS work together to provide highly accessible volumes available to several nodes in a failover cluster simultaneously.
FAQs about NTFS File System
1. How to format a NTFS drive for Mac?
If you want to use a NTFS drive on your Mac, you should erase it to another format at first. Connect the drive to your Mac and open Disk Utility.
Select the drive and click on Erase button. Select a file system such as APFS, HFS+, or exFAT and format it to the Mac-compatible system.
2. Is it possible to recover data from a formatted NTFS drive?
Yes, you can download a data recovery program, such as Donemax Data Recovery, to help in recovering deleted or lost data from a NTFS drive.
3. How to read & write to NTFS drives on macOS?
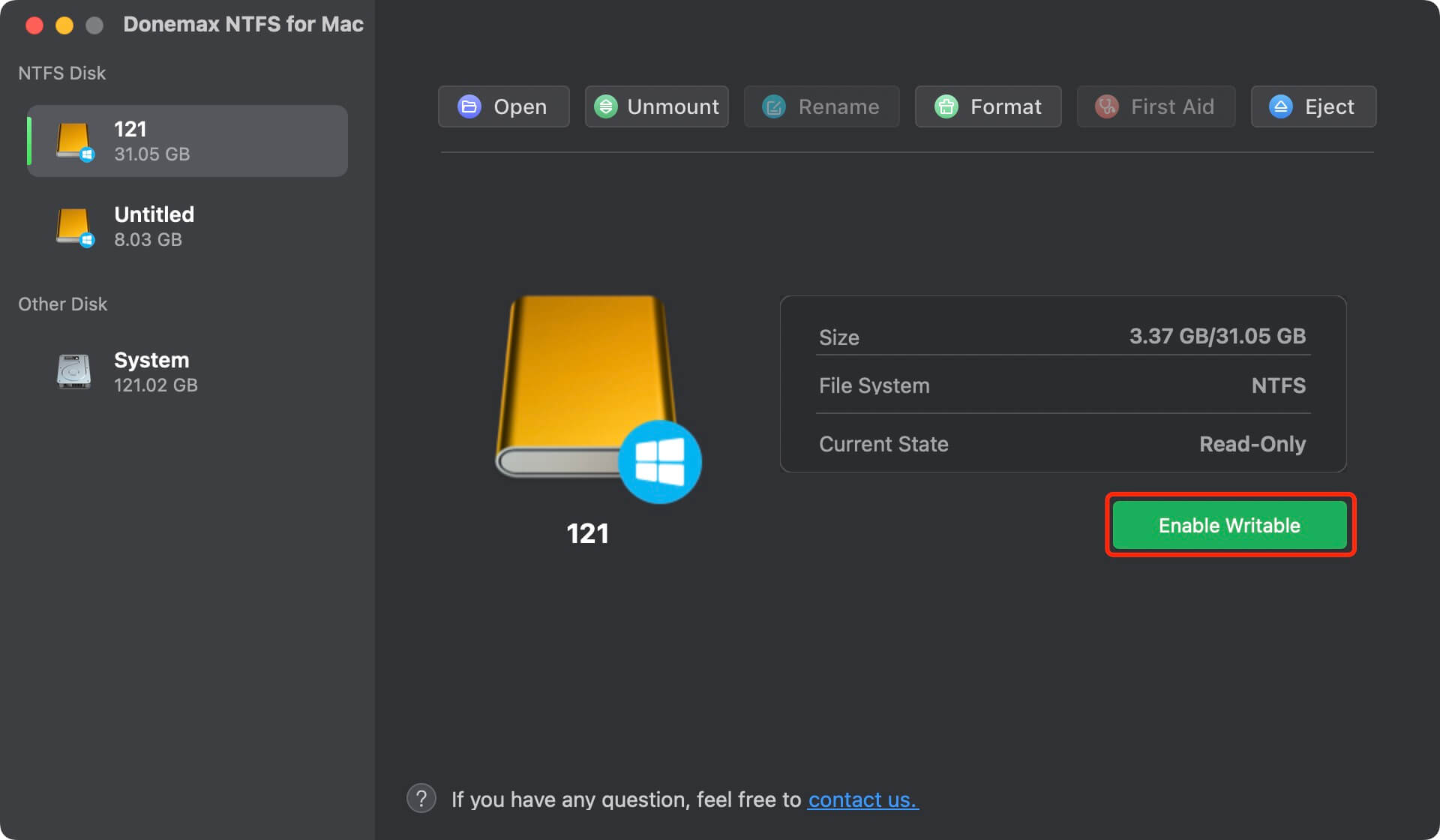
By default, NTFS drives are read-only on macOS. If you want to enable writable access for NTFS on Mac, you need to add NTFS driver for Mac. For example, you can use the software Donemax NTFS for Mac to enable full use of NTFS on macOS. The software offers the most reliable Microsoft NTFS driver for Mac and it works with latest macOS Tahoe 26. You can first download and install the software on your Mac. Also, ensure to approve the necessary permissions for the application.
You may need to restart the Mac after the installation and permission approvement. Then start the software and connect your NTFS drive to the Mac. Select the NTFS drive and click Enable Writable button. Then you can have full writable permissions to the NTFS drive on Mac.
Related Articles
- Apr 29, 2025What is SSD TRIM, How to Enable or Disable TRIM on SSD on Windows?
- Dec 19, 2024About SD Cards, SD Card Types, How to Format SD Cards
- Nov 27, 2024What is ReFS File System?
- May 26, 2025What's EFI Partition? Is It Safe to Delete the EFI Partition on Windows?
- Jul 24, 2024Apple Menu on Mac
- Jan 14, 2025About Mac Partition Scheme: GUID Partition Map, Master Boot Record, Apple Partition Map

Coco Lin
Coco has been a writer and a chief programmer at Donemax software since 2018. Over 10 years of experience of writing troubleshooting articles in the software industry, she is passionate about programming and loves to providing solutions to Windows and Mac users. Also she enjoys music and palying tennis in her free time.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems
Hot Donemax Products

Clone hard drive with advanced clone technology or create bootable clone for Windows/Mac OS.

Completely and easily recover deleted, formatted, hidden or lost files from hard drive and external storage device.

Certified data erasure software - permanently erase data before selling or donating your disk or any digital device.