Before we start: To make the applications run smoothly without the memory errors, ensure to follow the guide to fix the issue. Also, you can use the software Donemax DMcleaner for Mac to clear and optimize the Mac, which can help avoid the application memory errors.
PAGE CONTENT:
- What Does "Your System Has Run Out of Application Memory" Mean?
- Common Causes of Application Memory Exhaustion
- How to Identify Which App Is Using Too Much Memory
- Immediate Fixes When the Warning Appears
- Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix the Issue Permanently
- Advanced Troubleshooting for Power Users
- Preventing Application Memory Errors in the Future
- FAQs about Application Memory Errors on Mac
- Conclusion
Seeing the warning "Your system has run out of application memory" on a Mac can be alarming—especially if it appears repeatedly or interrupts important work. Many users assume this means their Mac is broken or critically low on RAM, but in reality, the issue is often related to how macOS manages memory rather than a single catastrophic failure.
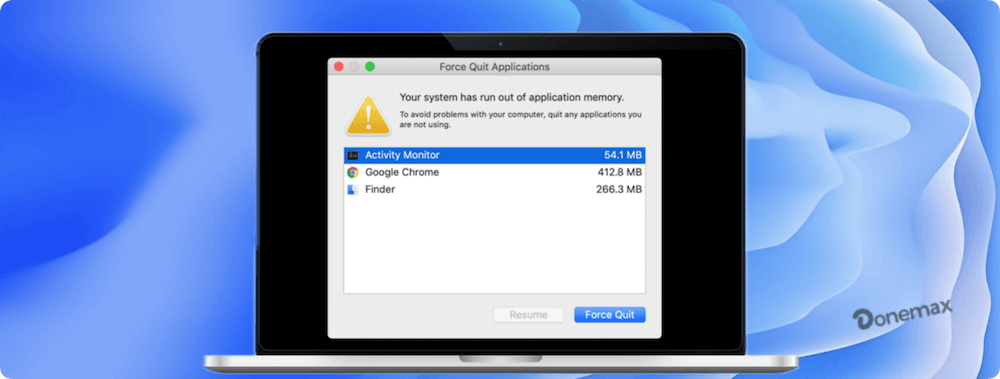
This article explains exactly what the error means, why it occurs, how to fix it step by step, and how to prevent it from happening again—whether you are a casual Mac user or a professional working with demanding applications.
What Does "Your System Has Run Out of Application Memory" Mean?
macOS uses a sophisticated memory management system designed to keep applications responsive even under heavy load. Instead of allowing the system to freeze, macOS actively monitors memory pressure and displays this warning when applications consume more memory than the system can comfortably handle.
Application memory includes:
- Physical RAM installed in your Mac
- Cached memory used for faster access
- Swap memory stored temporarily on disk when RAM is insufficient
When available RAM and swap capacity are exhausted—or when an application misbehaves and consumes excessive memory—macOS triggers the warning to protect system stability.
Importantly, this message does not always mean your Mac lacks enough RAM. In many cases, a single app, browser tab, or background process is responsible.
Common Causes of Application Memory Exhaustion
Understanding the root cause is critical before applying fixes.
1. Too Many Apps Running Simultaneously
Running multiple memory-intensive applications at the same time—such as browsers, video editors, IDEs, and design tools—can overwhelm available memory.
2. Browser Tabs and Extensions
Modern browsers are among the largest memory consumers on macOS. Each open tab runs as a separate process, and poorly optimized extensions can leak memory over time.
3. Memory Leaks in Applications
Some apps fail to release memory after it is no longer needed. These memory leaks accumulate, eventually triggering the warning even on high-end Macs.
4. Resource-Heavy Workflows
Tasks such as 4K video editing, large Photoshop files, Xcode builds, virtual machines, and Docker containers place sustained pressure on system memory.
5. Low Available Disk Space
macOS relies on free disk space for swap memory. If your startup disk is nearly full, the system cannot offload memory effectively.
6. macOS Bugs or Outdated Software
Occasionally, macOS updates or third-party apps introduce memory management bugs that worsen over time.
How to Identify Which App Is Using Too Much Memory
Before force-quitting applications blindly, identify the real culprit.
Using Activity Monitor
- Open Activity Monitor (Applications → Utilities).
- Switch to the Memory tab.
- Sort processes by Memory usage.
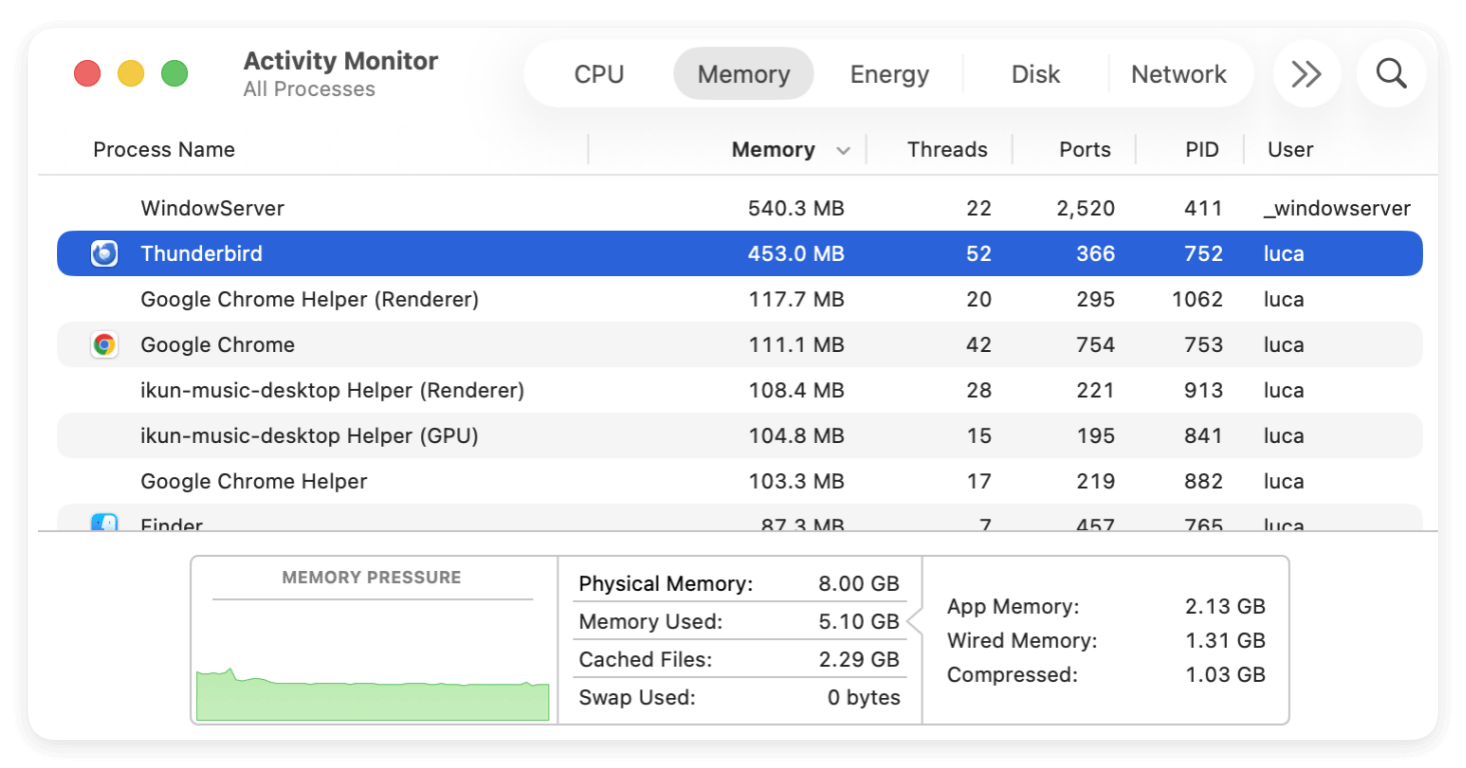
Key indicators to watch:
- Memory Pressure Graph
- Green: Normal
- Yellow: Elevated
- Red: Critical (likely to trigger warnings)
- Swap Used
High swap usage indicates RAM saturation.
- App Memory vs Cached Files
Cached memory can be reclaimed safely; app memory cannot.
If one application steadily increases memory usage without dropping, it likely has a memory leak.
Immediate Fixes When the Warning Appears
If the alert is already on your screen, act quickly but methodically.
1. Save Your Work
Always save documents before closing or force-quitting apps.
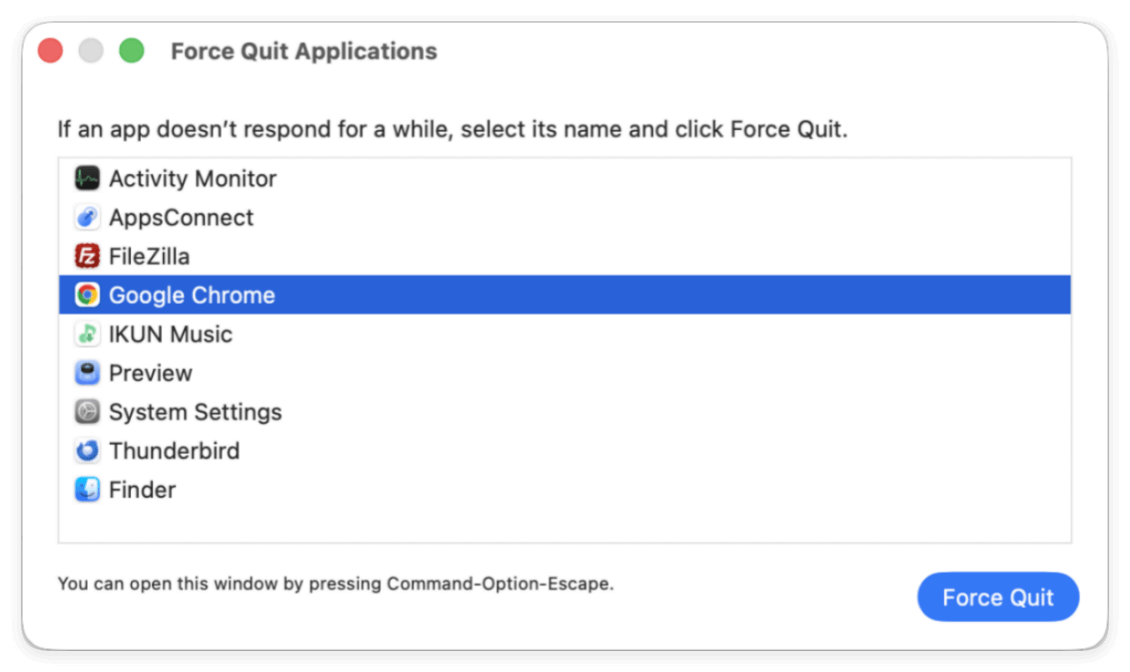
2. Force Quit High-Memory Applications
- Click the Apple menu → Force Quit
- Close the apps listed as using the most memory
3. Close Browser Tabs
Reducing tabs—especially media-heavy or web-app tabs—often provides instant relief.
4. Restart Your Mac
A restart clears RAM, resets background processes, and temporarily resolves most memory exhaustion issues.
These steps address symptoms, but not long-term causes.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix the Issue Permanently
Restart and Update macOS
Apple regularly fixes memory-related issues through system updates.
- Go to System Settings → General → Software Update
- Install the latest stable macOS version
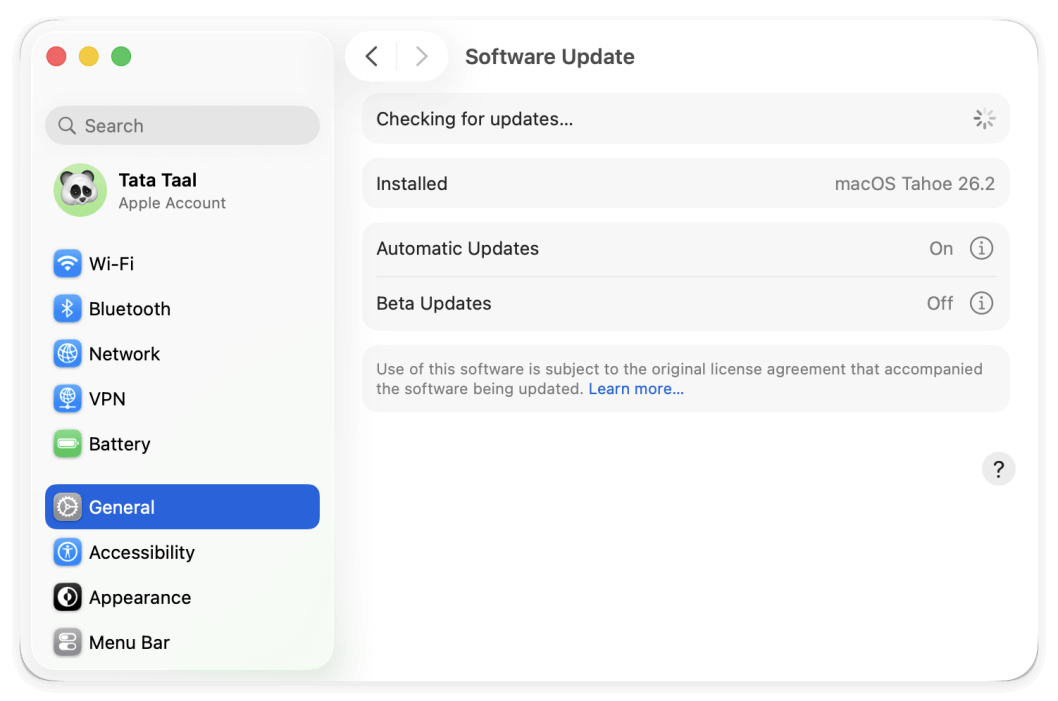
Outdated systems are more prone to memory leaks and inefficiencies.
Reduce Startup and Background Applications
Many apps run continuously without explicit user awareness.
- Open System Settings → General → Login Items & Extensions
- Remove non-essential apps from startup
- Disable unnecessary background helpers
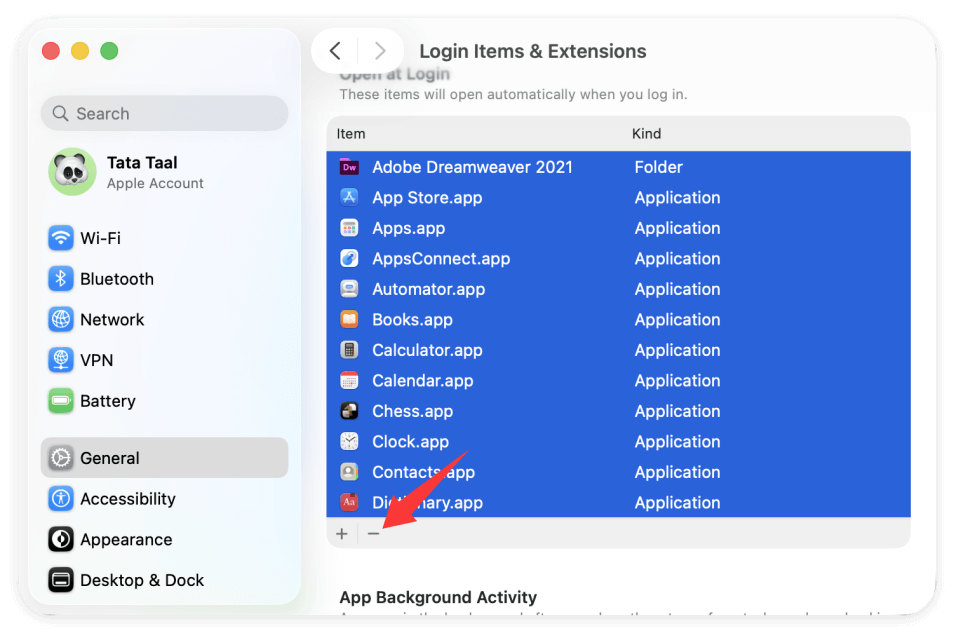
Fewer background processes reduce baseline memory consumption.
Optimize Browser Usage
Browsers deserve special attention.
Best practices:
- Keep fewer tabs open
- Use tab-suspension features
- Remove unused extensions
- Prefer lighter browsers for general browsing
If one browser consistently triggers memory warnings, consider switching.
Free Disk Space for Swap Memory
macOS requires free disk space to function as virtual memory.
Recommendations:
- Maintain at least 15–20% free disk space
- Delete unused files and apps
- Offload large media files to external storage
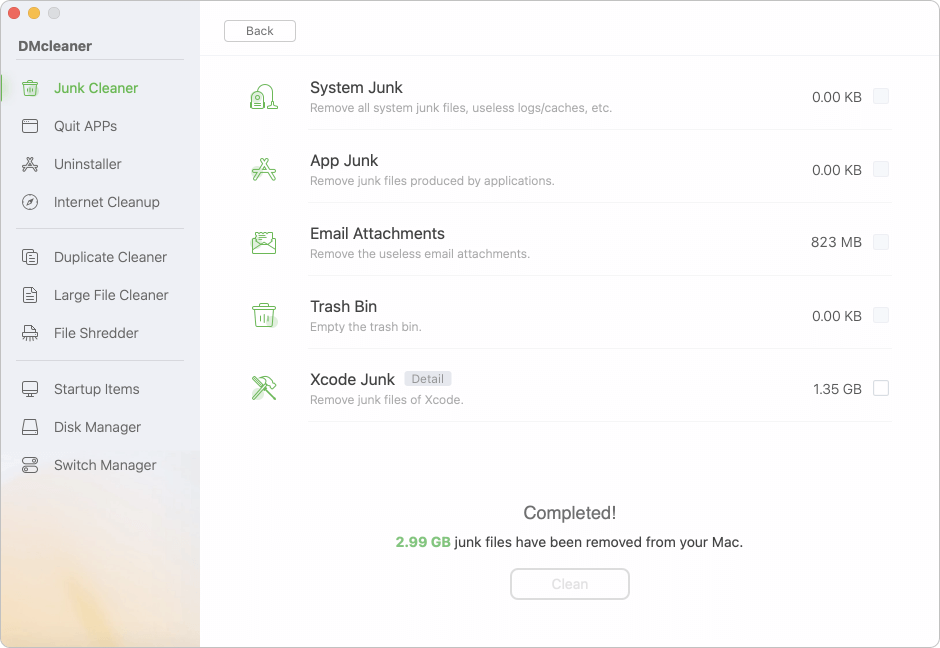
Low disk space can cause memory warnings even when RAM is sufficient. How to free disk space easily? We suggest you use the software Donemax DMcleaner for Mac. The software can deeply scan the Mac disk to search for the junk data.
First, you can use the mode Junk Cleaner to clear the system and application junk data. Also, the software offers other options to free more space on Mac, like uninstalling useless apps, clear duplicated or large files, etc.
Reset NVRAM and SMC (Intel Macs Only)
On Intel-based Macs, certain system controllers influence performance and memory behavior.
Resetting NVRAM/SMC can resolve persistent system-level issues. Apple Silicon Macs do not require these resets, as the process is handled automatically.
Advanced Troubleshooting for Power Users
If the issue persists, deeper investigation may be required.
Identify Persistent Memory Leaks
- Monitor the same app over several hours in Activity Monitor
- Look for continuous growth in memory usage
If confirmed:
- Update or reinstall the app
- Contact the developer
- Replace it with an alternative
Use Terminal Diagnostics (Optional)
Advanced users can inspect memory pressure and process usage via Terminal tools such as top or vm_stat. This is useful for diagnosing background services or headless processes.
Reinstall Problematic Applications
Corrupted application files or outdated frameworks can cause memory mismanagement. A clean reinstall often resolves the issue.
Apple Silicon vs Intel Macs: Does It Matter?
Yes, significantly.
Apple Silicon Macs
- Uses unified memory
- Aggressively swaps memory to SSD
- Appears efficient but can hit limits quickly on base models
Intel Macs
- Separate CPU and GPU memory
- Typically less aggressive swapping
- More dependent on physical RAM
On Apple Silicon Macs with 8 GB RAM, heavy multitasking can trigger memory warnings sooner than expected.
When Hardware Limits Are the Real Problem
Sometimes, software optimization is not enough.
Signs You Need More RAM
- Frequent memory warnings during normal workloads
- Constant high swap usage
- System slowdowns even after restarts
Modern Macs have non-upgradable RAM. If your workload has grown—such as professional editing, development, or virtualization—upgrading to a higher-memory Mac may be the only long-term solution.
Preventing Application Memory Errors in the Future
Adopt proactive habits to maintain system stability.
Best Practices
- Restart your Mac periodically
- Update apps and macOS regularly
- Avoid running redundant apps simultaneously
- Monitor memory usage during heavy tasks
- Match hardware to workload requirements
Preventative maintenance is far more effective than emergency fixes.
FAQs about Application Memory Errors on Mac
Conclusion
The "Your system has run out of application memory" warning on Mac is a signal—not a failure. It indicates that macOS is under memory pressure and needs intervention to maintain stability.
By identifying memory-hungry applications, optimizing browser and startup behavior, freeing disk space, and keeping macOS up to date, most users can eliminate this issue entirely. For professionals with demanding workloads, choosing the right hardware configuration is equally important.
With the right understanding and preventative steps, your Mac can remain fast, stable, and reliable—without constant memory warnings interrupting your work.
Related Articles
- Jun 16, 20252025 Best 8 Snipping Tools for Mac
- Mar 26, 2025Turn On or Turn Off Mac Firewall: A Complete Guide
- Sep 21, 2024Disk Utility Cannot Repair A Disk, Fix It Now
- Dec 09, 2024How to Add an External Hard Drive to Dock on Mac?
- Jul 19, 2025[11 Fixes] Fix iMessage Not Working on Mac, Not Syncing on Mac
- Apr 06, 2025Fix support.apple.com/mac/startup 3001F Error on Mac – A Comprehensive Guide

Christina
Christina is the senior editor of Donemax software who has worked in the company for 4+ years. She mainly writes the guides and solutions about data erasure, data transferring, data recovery and disk cloning to help users get the most out of their Windows and Mac. She likes to travel, enjoy country music and play games in her spare time.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems

