PAGE CONTENT:
In today's digital age, USB ports are everywhere - from the back of your desktop computer to the side of your laptop, in your car, and even on your smart TV. These small but mighty connectors have become an essential part of our digital lives. Whether it's charging a phone, transferring files, or connecting peripherals, USB ports are at the heart of modern computing. But what exactly are USB ports? How do they work? And why are there so many types and versions?
This article aims to answer all your questions about USB ports in a comprehensive, easy-to-understand manner. Let's dive into the world of USB technology.

What Is a USB Port?
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus, a standard developed in the 1990s to simplify the connection of peripheral devices to computers. Before USB, different devices often required different ports and drivers, making the process cumbersome. USB solved this by providing a standardized interface for data transfer and power delivery.
A USB port is the physical interface on a device that allows the connection of USB cables. The port facilitates two primary functions:
- Data Transfer - Between host devices (like computers) and peripherals (like flash drives or external hard drives).
- Power Supply - To charge or power connected devices such as smartphones, tablets, and accessories.
Today, USB ports are not only found on PCs but also on gaming consoles, smart TVs, car dashboards, and household gadgets.
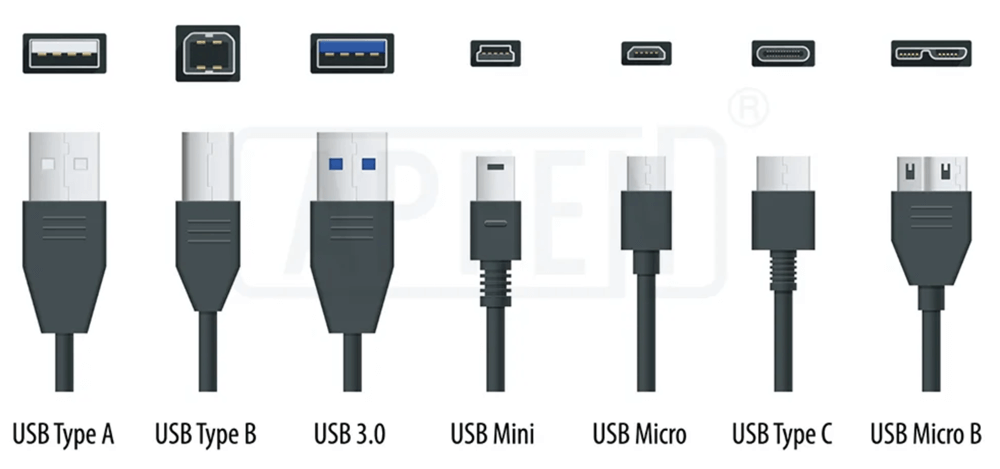
Types of USB Ports
Over time, USB ports have evolved in both shape and functionality. Here are the main types:
1. USB Type-A
This is the most common and widely recognized USB port. Rectangular in shape, it's found on computers, keyboards, flash drives, game consoles, and more. Type-A ports only fit in one orientation and are most often used for connecting peripherals.
2. USB Type-B
Type-B ports are usually square-shaped with a slanted top and are commonly used in printers, scanners, and external hard drives. This type is less common in consumer electronics.
3. Mini-USB
Smaller than Type-A and Type-B, the mini-USB was popular in early 2000s devices like digital cameras and older smartphones. It’s now largely obsolete.
4. Micro-USB
An even smaller connector than mini-USB, micro-USB became the standard for Android smartphones and other compact devices for years. It's still found in some accessories like wireless headphones and budget electronics.
5. USB Type-C
The newest and most versatile port, USB-C features a symmetrical, oval design that can be plugged in either way. It supports faster data transfer, higher power delivery, and even video output. USB-C is now the standard in most modern smartphones, laptops, and tablets.

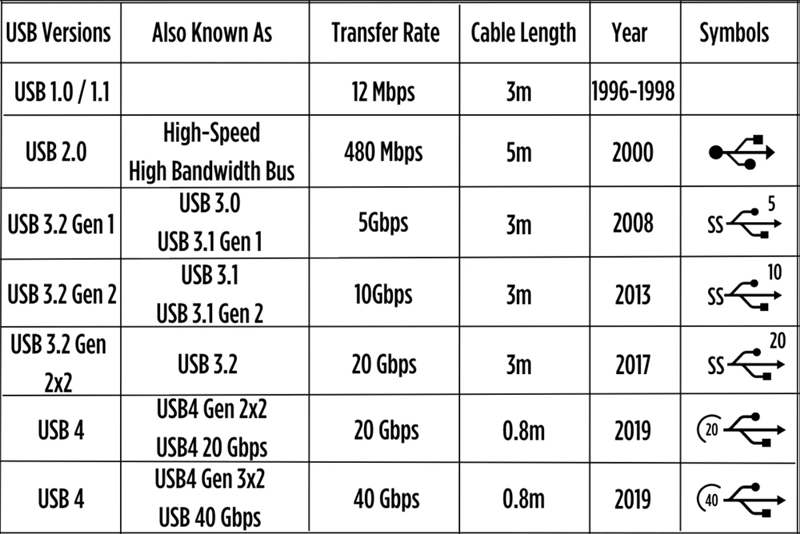
USB Versions and Speeds
Each USB port type may support different versions of the USB standard, which define data transfer speeds, power delivery capacity, and other features.
◾USB 1.0 and 1.1
Released: 1996 (1.0), 1998 (1.1)
Data Transfer Speed: 1.5 Mbps (Low-Speed), 12 Mbps (Full-Speed)
These were the original USB standards and marked the beginning of a universal connection format. USB 1.1 became more popular than 1.0 because of its reliability. It supported basic peripherals like keyboards, mice, and early printers. However, the speeds were too slow for large file transfers or media playback.
◾USB 2.0 (Hi-Speed)
Released: 2000
Data Transfer Speed: Up to 480 Mbps
Power Output: Up to 2.5W (5V, 0.5A)
USB 2.0 brought a significant jump in speed and became the most widespread standard in the 2000s. It enabled the use of external hard drives, digital cameras, and USB hubs. Although new standards have surpassed it, USB 2.0 is still used today—especially in low-power peripherals like keyboards and barcode scanners.
◾USB 3.0 (SuperSpeed USB)
Released: 2008
Data Transfer Speed: Up to 5 Gbps
Power Output: Up to 4.5W (5V, 0.9A)
This version introduced SuperSpeed USB, identifiable by its blue-colored port. It dramatically increased data transfer rates, making it suitable for high-definition video, large file backups, and SSDs. It also supported improved power efficiency and duplex (simultaneous send/receive) data transfer.
◾USB 3.1 (Gen 1 and Gen 2)
Released: 2013
Gen 1 Speed: 5 Gbps (same as USB 3.0)
Gen 2 Speed: 10 Gbps
Power Output: Up to 15W (via USB Power Delivery)
USB 3.1 Gen 2 doubled the transfer speed of USB 3.0 and introduced better encoding (128b/132b), reducing overhead and improving actual throughput. It also introduced wider support for USB Power Delivery (PD), enabling faster charging for smartphones, tablets, and even laptops.
A key change at this point was the confusing rebranding of USB versions:
- USB 3.0 became "USB 3.1 Gen 1"
- USB 3.1 became "USB 3.1 Gen 2"
This renaming created some confusion, but the main difference lies in the speed.
◾USB 3.2
Released: 2017
Speed: Up to 20 Gbps
Port Type: USB-C
Power Output: Up to 100W (with USB PD)
USB 3.2 uses multi-lane operation (2x10 Gbps lanes) over USB-C connectors, allowing for ultra-fast data transmission. It's commonly found in modern SSDs, gaming hardware, and high-end laptops. However, USB 3.2 requires both the cable and device to support dual-lane mode to achieve peak speeds.
Again, naming confusion persists:
- USB 3.1 Gen 2 became USB 3.2 Gen 2x1
- USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 refers to the new dual-lane 20 Gbps mode
◾USB4 (Unified Standard with Thunderbolt 3)
Released: 2019
Speed: Up to 40 Gbps
Port Type: USB-C only
Power Output: Up to 100W+
Notable Features:
- Fully backward compatible with USB 3.2 and USB 2.0
- Built-in support for DisplayPort and PCI Express (PCIe)
- Integrates Thunderbolt 3 functionality
USB4 is a game-changer. It merges the best features of USB and Thunderbolt and requires USB-C connectors. It supports fast external SSDs, 4K/8K video output, eGPU setups, and universal charging. USB4 is found on modern high-performance laptops like the MacBook Pro, Dell XPS, and HP Spectre.
USB Power Delivery (PD)
While earlier USB standards provided limited power (2.5W or 4.5W), modern devices require much more. USB Power Delivery solves this by negotiating voltage and current dynamically. With USB PD:
- Smartphones can charge faster (up to 27W or more)
- Laptops can charge via USB-C at 45W, 65W, or even 100W
- Monitors and docking stations can power laptops and transmit data/video at the same time
Backward Compatibility
One of USB's key strengths is backward compatibility. A USB 3.0 port can accept USB 2.0 devices, but the speed will default to the lower version.
Common Uses of USB Ports
USB ports serve a variety of purposes across devices and industries. Here are the most common applications:
1. Data Transfer
USB ports are most frequently used to transfer files between devices. For example, plugging a flash drive into a computer allows users to quickly copy photos, documents, and videos.
2. Charging Devices
USB ports also supply power. Smartphones, tablets, wireless headphones, and fitness trackers are all commonly charged via USB cables. USB-C ports in particular support faster charging speeds through Power Delivery (PD) standards.
3. Connecting Peripherals
Devices such as:
- Keyboards
- Mice
- Game controllers
- Webcams
- External hard drives; are all designed to connect to USB ports.
4. Media Playback and File Access
Smart TVs and car infotainment systems often feature USB ports to play videos, music, or display photos directly from a USB stick.
5. Booting and Operating Systems
USB drives can also be used to boot operating systems (like Windows or Linux) for installations or system recovery tasks.
6. Firmware Updates
Certain devices like routers, cameras, and even smart appliances can be updated via USB.
Troubleshooting USB Port Issues

Despite their reliability, USB ports can occasionally present issues. Here are some common problems and solutions:
1. Device Not Recognized
Causes:
- Faulty cable or port
- Corrupted USB driver
- Power management settings
Solutions:
- Try another USB port or device
- Disable USB selective suspend in Power Options
- Update USB drivers via Device Manager
2. Slow Transfer Speeds
Causes:
- Connecting a USB 3.0 device to a USB 2.0 port
- Low-quality USB cable
- Too many devices sharing bandwidth
Solutions:
- Use correct ports and high-speed cables
- Unplug other peripherals
3. Charging Issues
Causes:
- Insufficient power from USB 2.0 port
- Damaged cable or connector
Solutions:
- Use USB 3.0 or USB-C ports
- Try a different charging cable or adapter
4. Port Not Working at All
- Use compressed air to clean dust from the port
- Restart the device or check for BIOS/firmware updates
- Inspect hardware for damage
Future of USB Ports
USB technology continues to evolve to meet modern needs.
1. Rise of USB-C
USB-C is becoming the universal standard, replacing older USB types on laptops, tablets, and even desktop motherboards. Its reversibility, speed, and multi-functionality make it ideal for modern applications.
2. USB4 Standard
With speeds up to 40 Gbps and support for video output (DisplayPort, HDMI), USB4 is designed to compete with Thunderbolt. It's fully compatible with USB-C and is being adopted in high-end devices.
3. Integration with Thunderbolt
USB4 integrates Thunderbolt 3 features, allowing a single port to handle multiple tasks: display, charging, and data transfer. This simplifies connectivity and reduces port clutter on slim laptops and ultrabooks.
4. Regulatory Push for USB-C
The European Union has mandated USB-C as a common charging port for electronics by 2024. Other regions may follow, standardizing USB-C for environmental and consumer convenience.
Tips for Choosing the Right USB Port and Cable
- Match Device Needs to Port Type – High-speed external drives work best with USB 3.0 or above.
- Look for Port Labels – Many ports are labeled "SS" (SuperSpeed) for USB 3.x or have a lightning bolt for charging.
- Avoid Cheap Cables – Poor-quality USB cables can cause data corruption or overheating.
- Use Certified Accessories – Especially important for USB-C chargers and docks.
Conclusion
From their humble beginnings to their current role as versatile connectors for data, power, and multimedia, USB ports have transformed how we interact with technology. They connect our devices, charge our gadgets, and streamline our workflows. As USB-C and USB4 become more widespread, users can expect even faster, more efficient performance.
Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a casual user, or a professional working with complex setups, understanding USB ports helps you make better choices about devices, peripherals, and accessories. So next time you plug in that cable or connect that hard drive, you'll know exactly what's happening behind the scenes.
Related Articles
- Sep 12, 2025Windows Safe Mode: The Complete Troubleshooting Guide
- Mar 19, 2025What is U Disk? A Comprehensive Guide
- May 28, 2025What is Micro SDXC & Is it the Same as microSD?
- Nov 11, 2024Xcode for Mac Overview: What Is Xcode on Mac and Do You Need It?
- Jan 01, 1970About Text File (.txt), How to Open It on Windows or macOS
- Oct 24, 2025About Apple Silicon M5 Chip: M5 Chip vs. M4 Chip

Lucien
Lucien is a writer and a chief programmer of Donemax software who has worked in the company for 5+ years. He has written much of the content on the site and devotes to providing troubleshooting and solution for Windows and Mac users including disk cloning, data recovery, migration, eraser, error fixes.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems
Hot Donemax Products

Clone hard drive with advanced clone technology or create bootable clone for Windows/Mac OS.

Completely and easily recover deleted, formatted, hidden or lost files from hard drive and external storage device.

Certified data erasure software - permanently erase data before selling or donating your disk or any digital device.