Before we start: Donemax Data Eraser is a powerful disk wipe program. It offers erasure standards including DoD 5220.22-M and DoD 5220.22-M ECE to help in securely and permanently erasing data, wiping hard drives, erasing free disk space, etc. Once the data is erased by Donemax Data Eraser, the data is lost for good, can't be recovered by any method.
PAGE CONTENT:
In today's data-driven world, information security has become more critical than ever. From personal computers to enterprise servers, ensuring that sensitive data does not fall into the wrong hands is a top priority. While most users understand how to delete files or even format a drive, few realize that these actions often do not permanently remove data. This is where disk wiping comes in - and specifically, the Department of Defense (DoD) disk wipe standard.
In this article, we'll explore what the DoD disk wipe method is, why it's important, how it compares to other data destruction methods, and step-by-step instructions on how to use it.

What is DoD Disk Wipe?
The DoD disk wipe refers to a set of data sanitization methods that meet or exceed the standards outlined by the U.S. Department of Defense in directive 5220.22-M. Introduced in the early 1990s, this method was designed to securely erase data from magnetic storage devices to prevent any possibility of data recovery.
Unlike a simple delete or format, a DoD wipe overwrites each bit of data on a drive multiple times, typically with different patterns (like zeros, ones, and random characters), making it virtually impossible for any forensic tool to recover the original data.
Variants of the DoD Method
There are several versions of the DoD wiping standard, but the most common ones include:
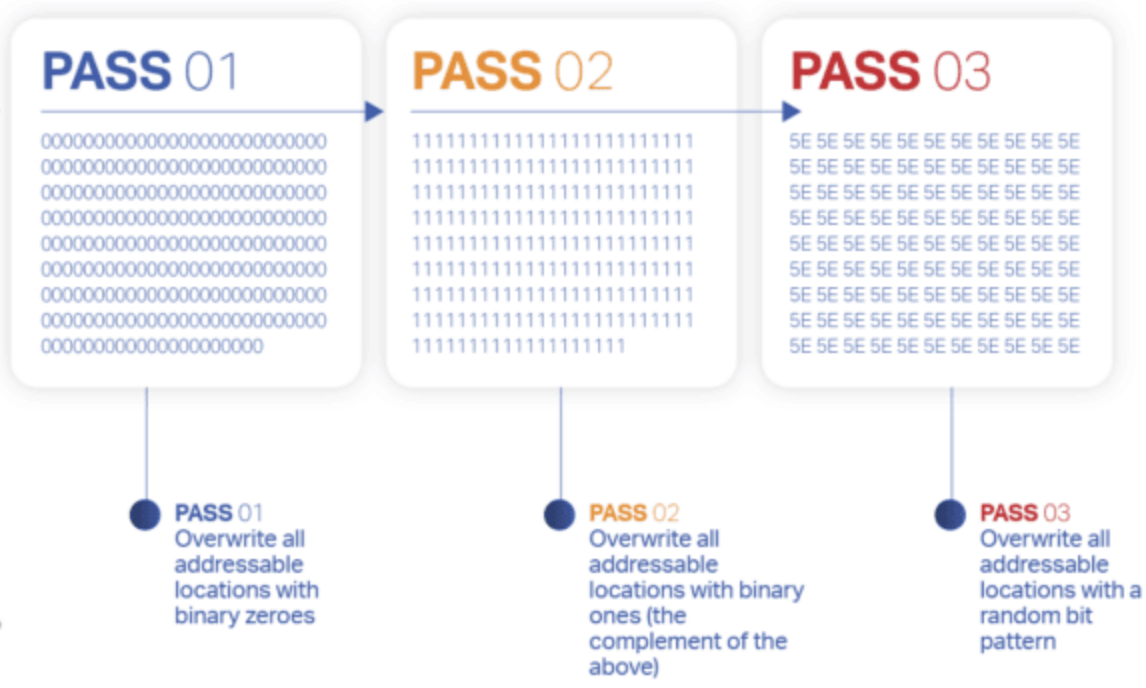
- DoD 5220.22-M (3-pass): Writes a character (e.g., 0), its complement (e.g., 1), then a random character, with verification.
- DoD 5220.22-M ECE (7-pass): More rigorous, repeating multiple overwrite patterns for enhanced security.
- Gutmann method (35-pass): Not officially a DoD standard but often cited in comparisons for extreme data sanitization.
Each pass ensures a higher level of certainty that the original data is irretrievable.
Why Use DoD Disk Wipe?
There are several compelling reasons to use DoD-compliant wiping techniques, especially in environments where data confidentiality is critical.
1. Security
Deleting files or formatting a drive does not remove the actual data; it only removes pointers to that data. With modern recovery software, deleted files can often be restored in minutes. A DoD disk wipe ensures the underlying data is completely overwritten.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and defense are bound by regulations (like HIPAA, GDPR, and others) that mandate proper data disposal methods. A DoD disk wipe meets or exceeds many of these regulatory requirements.
3. Privacy
Whether you're selling your computer, recycling a hard drive, or just cleaning up old equipment, using a DoD wipe ensures that your personal information - documents, photos, passwords, and browsing history - cannot be recovered by the next person who uses the device.
4. Enterprise Policy Enforcement
Organizations often implement data sanitization standards as part of their IT security policies. The DoD wipe standard is frequently adopted due to its reliability and historical credibility.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite its popularity and robust approach, the DoD disk wipe has its limitations.
1. Not Effective on SSDs
Solid State Drives (SSDs) work differently from traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). Due to wear-leveling algorithms, data may be stored in various locations and even preserved in over-provisioned memory areas not easily accessible. A DoD wipe might not overwrite all the actual data blocks on an SSD. For SSDs, Secure Erase (ATA command) or manufacturer-specific utilities are generally recommended.
2. Time-Consuming
The more passes a wipe involves, the longer it takes. A 1TB HDD can take several hours to wipe with a 3-pass DoD method, and even longer for 7 or 35 passes.
3. Drive Wear and Tear
Although this is more of a concern with SSDs, repeated writing can reduce the lifespan of the drive. If the drive is to be reused, this should be considered.
4. Overkill for Non-Sensitive Data
If you're erasing a drive that doesn't contain any sensitive or personally identifiable information, a simple full format or single-pass overwrite may be sufficient.
How to Perform a DoD Disk Wipe?
Performing a DoD disk wipe involves selecting the right tool, understanding your storage medium, and following precise steps to ensure complete data sanitization. Whether you're a casual user or an IT professional, here's a comprehensive guide on how to securely wipe your disk using DoD-compliant methods.
1. Identify the Storage Medium: HDD vs SSD
Before you begin, determine what kind of storage device you're wiping. The effectiveness of DoD methods differs between Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs).
- HDDs: Traditional spinning disk drives are ideal candidates for DoD wiping. Their sectors are physically overwritten during the wipe.
- SSDs: Due to wear-leveling algorithms and over-provisioned memory, some blocks on SSDs may not be overwritten by standard wiping tools. Instead, use tools that issue Secure Erase commands to the drive.
2. Using Built-in Tools (Basic Overwrite)
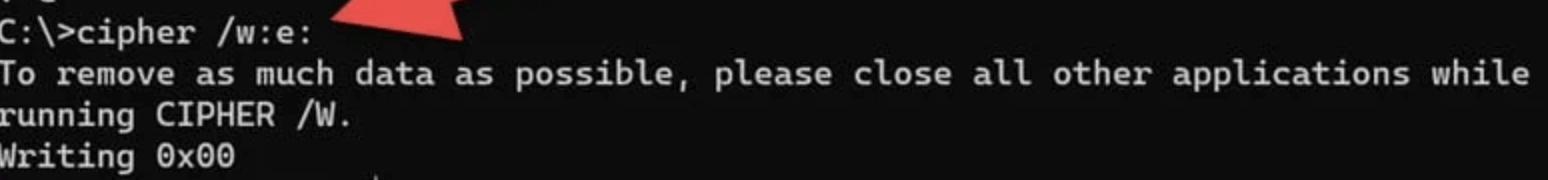
Windows: Cipher Command
The Cipher command isn’t a full DoD wipe, but it's useful for clearing deleted data from free space.
Steps:
- Open the Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Use the following syntax:
cipher /w:X:
![Department of Defense (DoD) disk wipe standard]()
Replace X: with your actual drive letter.
- The system will overwrite all free space with zeros, effectively wiping remnants of deleted files.
Limitations:
- Does not wipe the entire drive.
- Not DoD 5220.22-M compliant.
- Useful for desktops but not comprehensive for reformatting drives for resale or disposal.
3. Using Third-Party DoD Wipe Tool
Donemax Data Eraser is a powerful disk wipe program which offers DoD disk wipe methods for erasing data or wiping disks.
For example, you can follow the steps below to wipe a disk (SSD included) with Donemax Data Eraser:
Step 1. Download and install Donemax Data Eraser on your Windows computer or Mac computer.
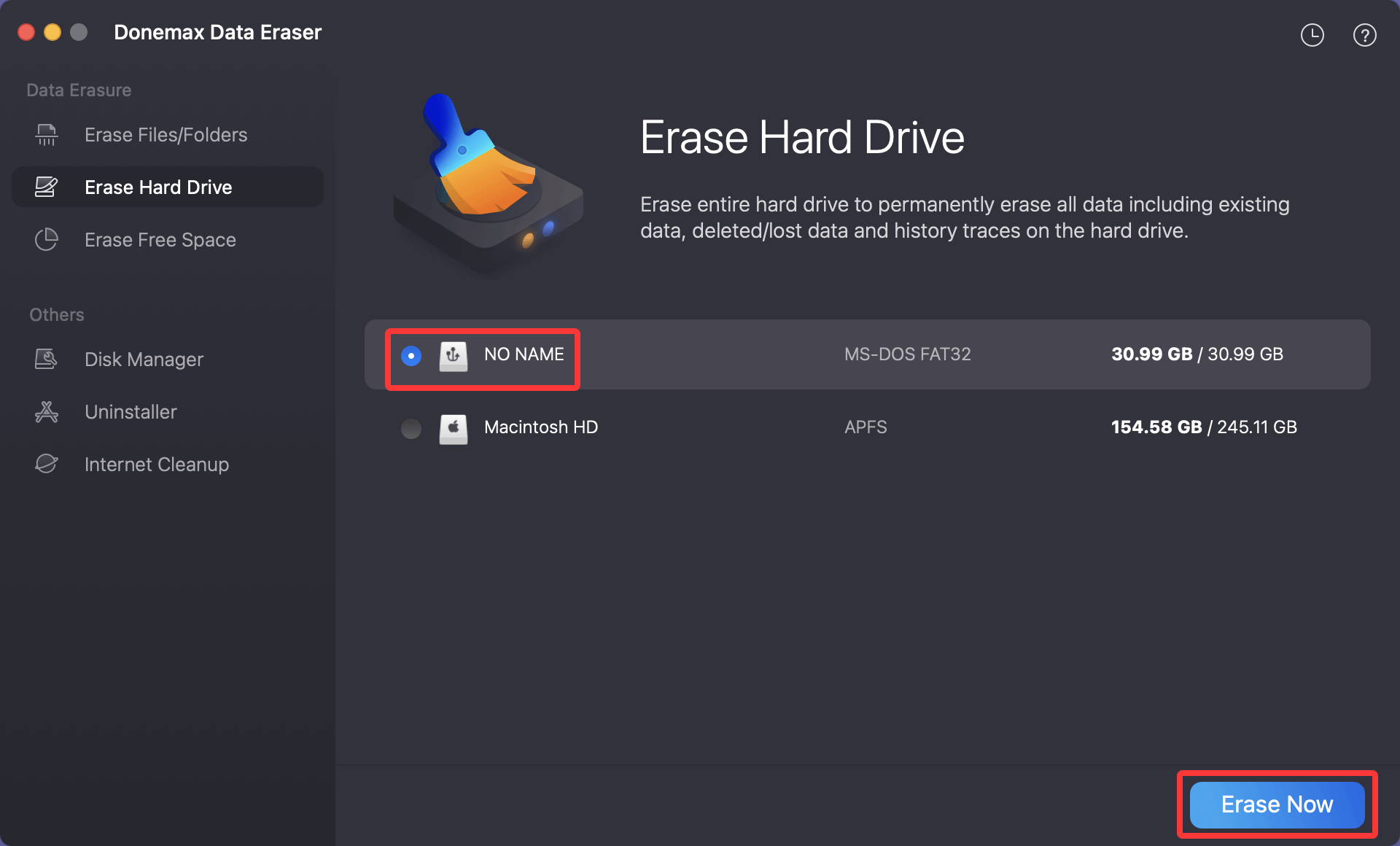
Step 2. Open Donemax Data Eraser, choose Erase Hard Drive mode for wiping a disk.
Step 3. Select the disk you want to erase, then click on Erase Now button.
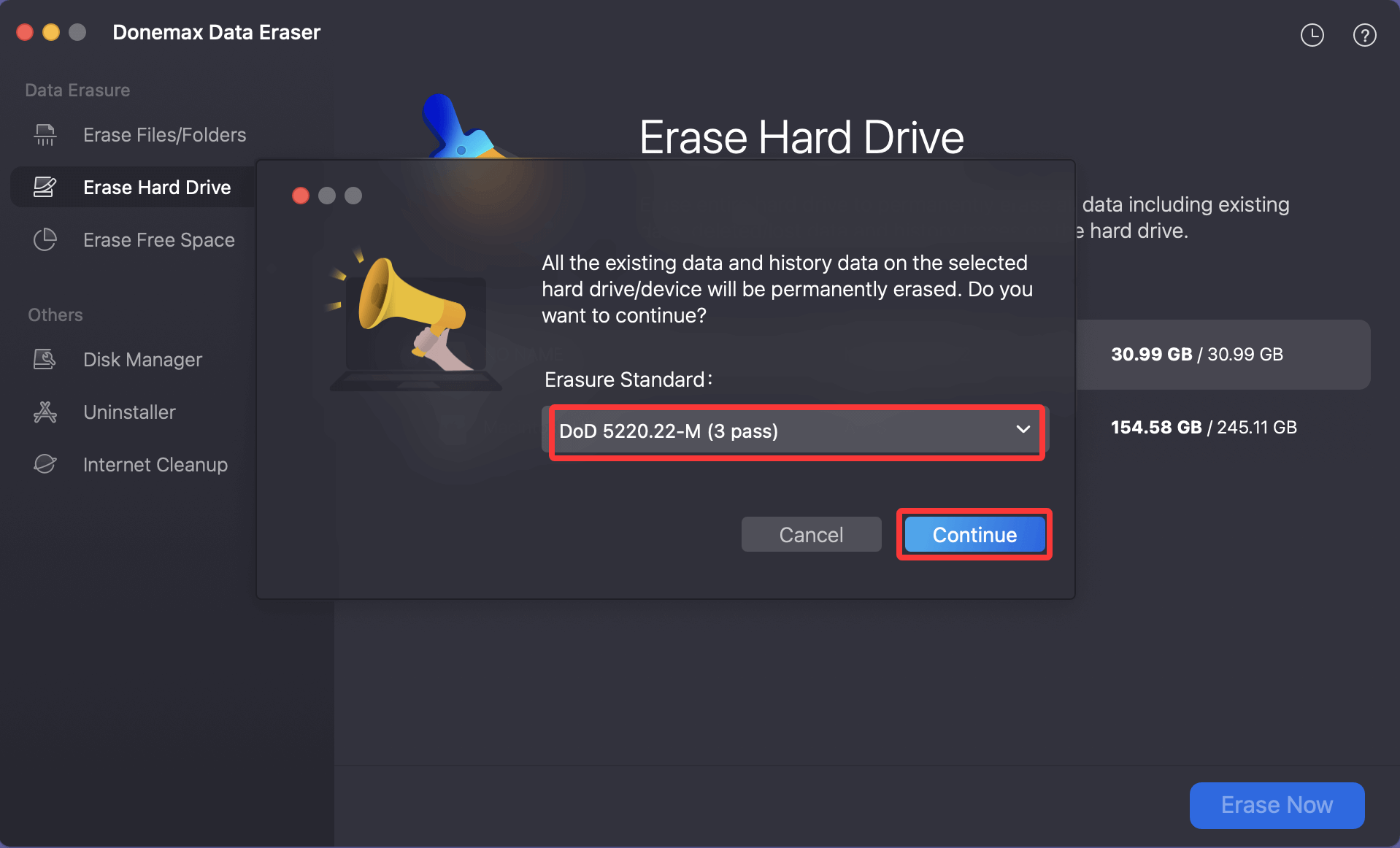
Step 4. Select DoD 5220.22-M or DoD 5220.22-M ECE to wipe the disk. Click on Continue button to start wiping the selected.
Once the process gets finished, all data stored on the disk is lost for good, can't be recovered by any method.
More DoD disk wipe programs:
▪️ DBAN (Darik's Boot and Nuke) - Best for Full Drive Wipes
DBAN is a free, open-source bootable tool that securely erases entire hard drives.
Features:
- Supports multiple wipe methods, including DoD 5220.22-M.
- Lightweight and fast for single-drive erasure.
How to Use DBAN:
- Download DBAN ISO from the official site.
- Use a tool like Rufus to create a bootable USB stick.
- Boot your system from the USB (change boot order in BIOS if needed).
- When DBAN loads, select:
- dodshort for 3-pass DoD wipe
- dod for 7-pass extended wipe
- Confirm and begin the wipe process.
Pros:
- Extremely effective for HDDs.
- Can be used without an OS.
Cons:
- Does not support SSDs.
- No log/report feature for compliance documentation.
▪️ Eraser (Windows GUI Tool) - Best for Selective Erasure
Eraser is a powerful, free Windows-based tool for securely deleting specific files or free space.
How to Use Eraser:
- Download and install Eraser.
- Launch the program and create a new task.
- Choose from these options:
- Delete specific files/folders.
- Wipe unused disk space.
- In "Task Properties," select DoD 5220.22-M (3 passes) or customize a multi-pass method.
- Run the task and review results.
Pros:
- User-friendly interface.
- Ideal for wiping free space or targeted files.
- Customizable erase methods.
Cons:
- Not suited for wiping entire drives if the OS is still installed on it.
▪️ CCleaner (Windows/macOS) – Basic DoD-Style Wiping
CCleaner includes a "Drive Wiper" function that supports DoD-style multi-pass overwriting.
Steps to Wipe a Drive in CCleaner:
- Go to Tools > Drive Wiper.
- Choose:
- What to wipe: Free Space Only or Entire Drive.
- Security level: 1-pass, 3-pass (DoD), 7-pass, or 35-pass.
- Select the target drive and click Wipe.
Pros:
- Easy to use for beginners.
- Offers a balance between speed and security.
Cons:
- Lacks advanced features for enterprise use.
- Less control over verification and logging.
▪️ Blancco Drive Eraser – Enterprise Grade Tool
Blancco is a paid solution used by corporations and data centers for certified data destruction.
Features:
- Supports DoD, NIST, and 20+ global standards.
- Provides reports and certificates for auditing.
- Works with HDDs, SSDs, NVMe, and RAID arrays.
How to Use:
- Install or boot from the Blancco environment.
- Select the target drives and wiping method (e.g., DoD 3-pass).
- Start the erasure process.
- Download and save the report for compliance purposes.
Pros:
- Fully compliant with industry regulations.
- Professional support and detailed logs.
Cons:
- Paid software; best for businesses and IT administrators.
4. Wiping SSDs with DoD-Equivalent Techniques
As previously mentioned, standard DoD overwriting doesn't guarantee full sanitization on SSDs. Instead, use these approaches:
Manufacturer-Specific Tools:
- Samsung Magician (for Samsung SSDs)
- Intel SSD Toolbox
- Crucial Storage Executive
- SanDisk SSD Dashboard
These tools issue the Secure Erase command, instructing the drive’s firmware to reset all cells to factory condition.
💡 Note: These utilities often require booting into a special mode and may temporarily disable BitLocker or BIOS settings like Secure Boot.
5. Creating a Bootable USB for Disk Wiping
Many secure wiping tools require bootable media to function outside the operating system (especially when wiping the system drive).
How to Create a Bootable USB with Rufus:
- Download the wiping software ISO (e.g., DBAN).
- Download and run Rufus.
- Select your USB drive and ISO file.
- Click Start and wait until the bootable drive is created.
- Reboot your system and boot from the USB to begin wiping.
6. Tips for Safe and Effective Disk Wiping
- Use Verification: Some tools offer a verification phase to ensure that overwrites were successful. Always enable this when available.
- Double-Check Drive Selection: Selecting the wrong drive can result in irrecoverable loss of critical data.
- Disconnect Other Drives: If wiping from a bootable tool, unplug other storage devices to avoid accidental wipes.
- Consider Logging: If you need to comply with standards like HIPAA, NIST, or GDPR, choose tools that generate logs or certificates of destruction.
Best Practices for Secure DoD Data Wiping
To ensure your data is truly gone and you're staying compliant, follow these best practices:
1. Back Up First
Before wiping any drive, ensure you’ve backed up all critical files elsewhere. Once wiped, recovery is virtually impossible.
2. Verify Completion
Use tools to verify that the wiping process was successful. Some tools offer logs or reports you can keep for records.
3. Combine Methods (if needed)
In high-security scenarios, it's a good idea to perform a DoD wipe followed by physical destruction (like degaussing or shredding).
4. Maintain Compliance Logs
If you're an organization, ensure logs or certificates of data destruction are saved for auditing and compliance checks.
5. Use Vendor Tools for SSDs
For SSDs, check with the manufacturer for a utility that supports secure erase. Examples include:
- Samsung Magician
- Intel SSD Toolbox
- Crucial Storage Executive
Conclusion
The DoD disk wipe method is one of the most recognized and effective techniques for securely erasing data from hard drives. By using multiple overwrite passes, it ensures that data cannot be recovered, even with advanced forensic tools. While it's more time-consuming than a simple format or delete, it provides peace of mind - especially when disposing of or selling a storage device that once held sensitive information.
That said, it's essential to understand the limitations of DoD wipes, particularly when dealing with SSDs, and to choose the right tool and method based on your needs. Whether you're a home user wanting to sell an old laptop or a business needing to comply with regulatory data disposal standards, the DoD disk wipe remains a solid choice for secure data destruction.


Donemax Data Eraser
One of the best data erasure programs for permanently erase data from PC, Mac, HDD, SSD, USB drive, digital camera and other devices. Once the data is erased, it is lost for good, cannot be recovered by any method.
Related Articles
- Sep 11, 2025Wipe Operating System and User Data from My Computer
- Jun 09, 2025About 'Reset This PC': How to Use 'Reset This PC' to Factory Reset a Computer
- May 10, 2025How to Wipe Sabrent Rocket External SSD?
- Mar 05, 2024What to Do Before Selling A HP Laptop?
- May 30, 2025How to Wipe A Drive with CCleaner?
- Jan 10, 2024Windows 11 Factory Reset: Step-by-step Detailed Guide

Charles
Charles, who lives in Sydney, Australia, is an editor & writer of Donemax Team. He is good at writing articles related with Apple Mac computers, Windows operating systems, data recovery, data erasure, disk clone and data backup, etc. He loves reading and playing tennis in his spare time and is interested in testing new digital devices such as mobile phones, Macs, HDDs, SSDs, digital cameras, etc.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems