Before we start: The deleted/formatted data is not lost permanently and can be easily recovered by data recovery software. If you want to prevent the data from being recovered by data recovery method, you can use Donemax Data Eraser to wipe free disk space of the drive and permanently erase all deleted/formatted/lost data.
PAGE CONTENT:
In today's digital age, the data we store on our devices holds immense value, not just personally, but often professionally as well. When we delete files or format our devices, the expectation is that the data is gone for good. However, this is not always the case. In fact, most deleted or formatted data can be recovered using specialized software or techniques. This can pose significant security risks, especially when you're disposing of or repurposing a device that once contained sensitive information.
To ensure that deleted or formatted data is unrecoverable, we need to understand how data deletion works, why it can be recovered, and how to implement more secure methods of data destruction. This article will explore the different methods to ensure that your deleted and formatted data cannot be recovered, from software solutions to physical destruction.

Understanding Data Deletion and Formatting
▪️ What Happens When You Delete Files?
When you delete a file on your computer, you're not truly erasing the data from the storage device. Instead, the file's entry in the FAT or MFT is removed, marking the space occupied by the file as free. The data still exists in the same location on the disk, but the system no longer knows where to find it. Until this space is overwritten with new data, the deleted file remains recoverable.
This is why data recovery software can often retrieve deleted files even after they've been removed from the recycle bin.
▪️ What Happens During Formatting?
Formatting a disk or partition involves setting up a new file system, which means creating a new structure for storing data. During a quick format, only the file system's structure is erased, and the data itself remains untouched. The drive's space is marked as available, but the data still exists until overwritten.
A full format, on the other hand, overwrites the data once, which can make recovery more difficult but doesn't guarantee that the data is permanently erased.
Why Deleted or Formatted Data Can Be Recovered
Storage devices can be searched for traces of erased or formatted contents using data recovery software. These tools exploit the fact that, unless the space has been overwritten by new data, the file's remnants are still physically present on the storage medium.
For instance, tools like Donemax Data Recovery, Recuva, EaseUS Data Recovery, and PhotoRec can recover deleted files by scanning the disk sectors where the data was once stored. The more recent the deletion and the fewer new files written to the drive, the higher the chances of a successful recovery.
Moreover, even after a full format, most of the data on the disk remains recoverable for some time, as the format only partially wipes the storage medium. It is not a definitive erasure method.

How to Recover Deleted/Formatted and Lost Data?
Data recovery software can deeply scan your drive or device and help find/recover all deleted, formatted and lost data.
Methods to Make Deleted/Formatted Data Unrecoverable
Method 1. Overwriting the Storage Space
One of the most effective ways to ensure that deleted or formatted data is unrecoverable is by overwriting the data on the storage device. When data is overwritten, new information is written over the areas where the deleted files once existed, effectively making the old data irretrievable.
1. Disk Wiping Tools
Several disk-wiping tools are available to securely overwrite data on hard drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and other storage devices. Popular tools include:
- Donemax Data Eraser: One of the best disk wipe programs. Securely wipe free disk space of the drive, overwrite and erase all deleted/formatted/lost data permanently.
- DBAN (Darik's Boot and Nuke): A free tool for erasing entire hard drives by overwriting all data multiple times.
- Eraser: A free, open-source tool that securely deletes files and folders by overwriting them.
- CCleaner Drive Wiper: A paid feature of CCleaner that allows users to securely wipe free space or entire drives.
2. Multiple Overwrite Passes
Overwriting data once may not be sufficient, especially for advanced data recovery methods. To ensure that data is irrecoverable, several overwrite passes are recommended. The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) 5220.22-M standard, for example, recommends overwriting a drive three times with different patterns of data.
For even greater security, the Gutmann Method suggests 35 passes of random data, although it is generally considered overkill for most users.
Method 2. Secure Format Options
As mentioned earlier, a standard quick format does not erase the data. If you want to securely format a drive, you should use secure formatting options available in various operating systems.
1. Full Format
In both Windows and macOS, performing a full format as opposed to a quick format will overwrite the data once, making recovery more challenging. While this is more secure than a quick format, it's still not foolproof.
2. OS-Specific Secure Formatting
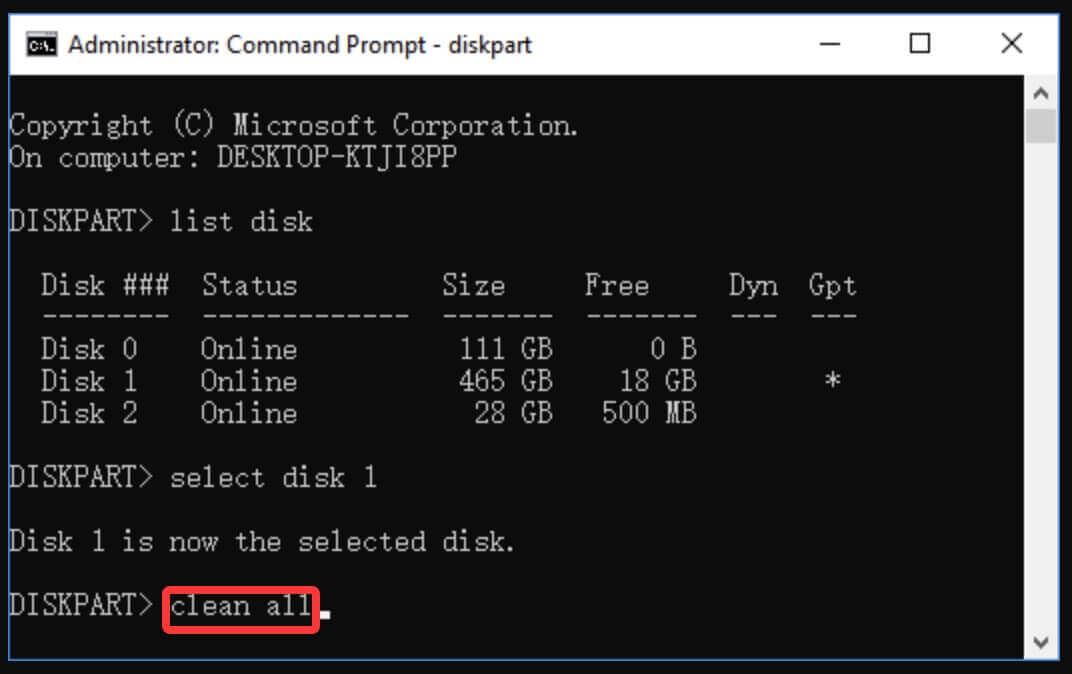
- Windows: Using the built-in Diskpart utility, you can issue the "clean all" command, which will overwrite all sectors on the drive. This is a secure way to format a drive and ensure the data is more difficult to recover.
![deleted or formatted data is unrecoverable]()
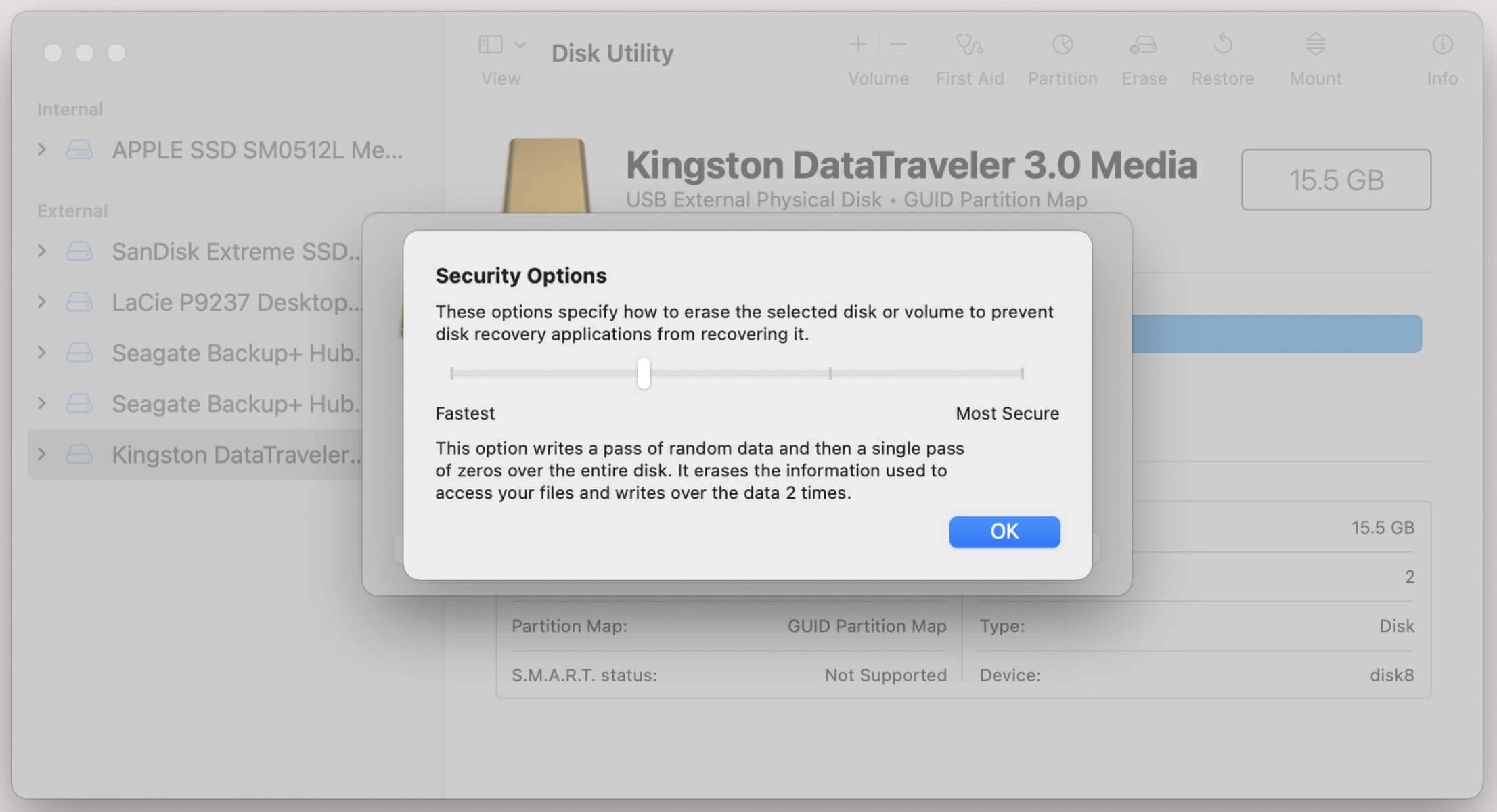
- macOS: The Disk Utility app offers a "Security Options" option that overwrites the drive once to make recovery more difficult.
![deleted or formatted data is unrecoverable]()
Method 3. File Shredding Tools
If you only need to delete individual files rather than wiping an entire drive, file shredding tools can securely delete files by overwriting them multiple times before they are removed from the system.
Tools like Donemax Data Eraser, BleachBit, File Shredder, and SecureDelete allow users to securely delete files by replacing the data with random characters multiple times. This ensures that the original data cannot be recovered, even by advanced recovery tools.
For example, if you want to permanently wipe all deleted/formatted data from a drive, you can use Donemax Data Eraser to wipe free disk space of the drive.
Step 1. Download and install Donemax Data Eraser on your computer.
Step 2. Open Donemax Data Eraser, then choose Erase Free Space mode. Select the target drive, then click on Erase Now button.

It will securely and permanently erase all deleted/formatted/lost data from the drive.
More Tips About Data Erasure
OS-Specific Tips for Secure Data Erasure
Each operating system has its own tools and methods for securely deleting or erasing data.
▪️ Windows
In Windows, you can use BitLocker to encrypt your drives, which adds an additional layer of security. When the data is encrypted, even if someone tries to recover it, they’ll need the encryption key. Additionally, using Diskpart with the "clean all" command will ensure that the data is overwritten securely.
▪️ macOS
macOS users can use FileVault to encrypt their drives. This means that even if the drive is formatted, the encrypted data will be useless without the correct password. When using Disk Utility, the "Secure Erase" function is available to overwrite the data on the drive.
For SSDs: Special Considerations
SSDs (Solid State Drives) present a unique challenge when it comes to data erasure. Unlike HDDs, SSDs use flash memory cells to store data, which can be accessed and erased at the chip level. Overwriting data on an SSD is less effective due to the wear-leveling technology that ensures data is stored across multiple locations on the drive.
▪️ TRIM Command
TRIM is an essential feature for modern SSDs, designed to maintain performance and extend the lifespan of the drive. However, its role in making deleted data unrecoverable is a bit nuanced.
How TRIM Works:
When data is deleted from an SSD, the operating system sends a signal to the SSD informing it that the blocks holding that data are no longer in use and can be erased. This is where TRIM comes into play. Unlike HDDs, which retain deleted data until it is overwritten by new data, SSDs require a command to tell them to clean up unused blocks. Without TRIM, an SSD might hold onto deleted data longer than necessary, leaving room for recovery tools to retrieve it.
When TRIM is active, it helps maintain the SSD's speed and lifespan by cleaning up unused sectors more efficiently. Essentially, it tells the drive’s controller that certain areas no longer contain valid data, so they can be wiped or marked as free for future use.
▪️ Secure Erase
Secure Erase is a term used to describe specific commands that physically wipe data from an SSD, leaving no recoverable traces behind. Unlike TRIM, Secure Erase is designed explicitly for the purpose of making data irretrievable by overwriting every sector of the drive.
How Secure Erase Works:
The Secure Erase command works by resetting all memory cells to their factory state. It completely overwrites the sectors where your data once existed, making it impossible to recover. This method ensures that the drive is essentially "reset" to its default state and no remnants of the original data are left behind.
In addition to the ATA Secure Erase command, some manufacturers use proprietary methods to enhance the security of the erase process. These may include multiple overwriting passes, though the effectiveness of such passes on SSDs is debatable due to the nature of how flash memory functions.
Physical Destruction (Last Resort)
If the data is so sensitive that no software solution is adequate, physical destruction may be the only guaranteed method to ensure data is unrecoverable. This is often used in high-security situations, such as government or military settings.
▪️ Techniques for Physical Destruction
- Drilling: Drilling through the drive's platters (in the case of HDDs) physically damages the disk, making data retrieval impossible.
- Shredding: Using an industrial shredder to destroy the drive completely.
- Degausser: A degausser uses powerful magnets to erase data stored on magnetic media like hard drives.
While physical destruction is an extreme measure, it is the only surefire way to destroy data if software methods are unavailable or insufficient.
Best Practices for Data Sanitization
To ensure that deleted and formatted data is truly unrecoverable, you should follow these best practices:
- Use the right tool for your specific storage device (HDD, SSD, USB drive).
- Encrypt sensitive data before storage or deletion to add an extra layer of security.
- Perform multiple overwriting passes to ensure no trace of the original data remains.
- Regularly wipe free space on your drives to prevent residual data from being recovered.
- When in doubt, destroy the drive physically, especially if you need to be absolutely sure that no data can be recovered.
Conclusion
Ensuring that deleted and formatted data is unrecoverable is a critical step in protecting your privacy and security. From using specialized software like disk-wiping tools and file shredders to leveraging built-in secure erasure functions in operating systems, there are various methods to make data irreversible. For SSDs, ensure that TRIM is enabled and use manufacturer-specific secure erase commands. In the most extreme cases, physical destruction remains the only guaranteed solution.
By following these guidelines and choosing the right tools, you can ensure that your sensitive data remains securely erased and inaccessible to others.


Donemax Data Eraser
One of the best data erasure programs for permanently erase data from PC, Mac, HDD, SSD, USB drive, digital camera and other devices. Once the data is erased, it is lost for good, cannot be recovered by any method.
Related Articles
- Jan 28, 2024How to Wipe Toshiba External Hard Drive?
- Jun 05, 2024How to Reset Microsoft Surface to Its Factory Settings?
- May 06, 2024How to Factory Reset Gopro HERO12 Black Before Selling or Donating It?
- Dec 13, 20242025 Comprehensive Guide: Introduction to Data Erasure Standards
- Jun 28, 2024How to Factory Reset Razer Computer?
- Feb 17, 2025How to Dispose of a Dying Hard Drive?

Steven
Steven has been a senior writer & editor of Donemax software since 2020. He's a super nerd and can't imagine the life without a computer. Over 6 years of experience of writing technical solutions and software tesing, he is passionate about providing solutions and tips for Windows and Mac users.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems